Drug Trials Snapshot: NERLYNX
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the NERLYNX Package Insert for complete information.
NERLYNX (neratinib)
(ner links)
Puma Biotechnology, Inc.
Approval date: July 17, 2017
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
NERLYNX is a drug for treatment of an early stage HER2 -positive breast cancer in women who have been previously treated with the medicine trastuzumab. NERLYNX is given as an extended adjuvant therapy, a form of therapy that is taken after an initial treatment to further lower the risk of the cancer coming back.
How is this drug used?
Six NERLYNX tablets (total of 240 mg) are taken once a day, with food. NERLYNX is usually taken for 1 year. During the first two months of treatment, patients should also take a drug to manage diarrhea called loperamide, and thereafter as needed.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Women taking NERLYNX experienced a longer time period before their cancer returned, in comparison to women who took placebo.
Information on overall survival of these women is not available at this time.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Table 2 shows invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) defined as the time between the date of randomization to the first occurrence of invasive recurrence (local/regional, ipsilateral or contralateral breast cancer), distant recurrence, or death from any cause, with 2 years and 28 days of follow-up.
Table 2. Efficacy iDFS – Trial 1 (Intent-to-Treat Population)
| Number of Events/ Total N (%) | iDFS at 24 months1 | Stratified2 HR (95% CI) | p-value3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NERLYNX | Placebo | NERLYNX | Placebo | |||
| 67/1420 (4.7) | 106/1420 (7.5) | 94.2 (92.6, 95.4) | 91.9 (90.2, 93.2) | 0.66 (0.49, 0.90) | 0.008 | |
HR=Hazard Ratio
1 Kaplan-Meier estimate
2 Stratified by prior trastuzumab (concurrent vs. sequential), nodal status (0-3 positive nodes vs. ≥4 positive nodes), and ER/PR status (positive vs. negative)
3 Stratified log-rank test
NERLYNX Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The trial included only women therefore sex differences cannot be determined.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in response among races could not be determined.
- Age: NERLYNX worked similarly in patients above and below 60 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
Table 3 shows the efficacy results by relevant demographic and geographic subgroups. These exploratory analyses were conducted without adjusting multiple comparisons.
Table 3. Subgroup Efficacy Analyses
| Population | Number of Events/ Total N (%) | KM Estimate for iDFS at 24 months (%, 95% CI) | Unstratified HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NERLYNX | Placebo | NERLYNX | Placebo | ||
| Age Group | |||||
| 35> | 5/46 (10.9) | 12/55 (21.8) | 86.9 (71.1, 94.4) | 73.3 (57.7, 83.9) | 0.43 (0.14, 1.17) |
| 35-49 years | 28/523 (5.4) | 40/515 (7.8) | 93.4 (90.5, 95.4) | 91.4 (88.5, 93.6) | 0.71 (0.44, 1.15) |
| 50-59 years | 17/497 (3.4) | 33/488 (6.8) | 95.8 (93.3, 97.4) | 92.7 (89.9, 94.8) | 0.53 (0.29, 0.94) |
| ≥ 60 years | 17/354 (4.8) | 21/362 (5.8) | 93.8 (90.3, 96.1) | 93.7 (90.5, 95.9) | 0.93 (0.48, 1.76) |
| Race | |||||
| White | 53/1165 (4.5) | 85/1135 (7.5) | 94.4 (92.8, 95.7) | 91.9 (90.0, 93.4) | 0.65 (0.46, 0.91) |
| Asian | 12/188 (6.4) | 16/197 (8.1) | 92.2 (86.7, 95.5) | 91.1 (85.8, 94.5) | 0.78 (0.36, 1.64) |
| Black or African American and Other | 2/67 (3.0) | 5/88 (5.7) | 96.4 (86.5, 99.1) | 93.7 (85.5, 97.3) | 0.57 (0.08, 2.62) |
| Region | |||||
| North America | 23/519 (4.4) | 28/477 (5.9) | 94.6 (91.9, 96.4) | 93.7 (91.0, 95.6) | 0.81 (0.46, 1.40) |
| Western Europe, Australia, and South Africa | 24/487 (4.9) | 38/532 (7.1) | 93.9 (91.0, 95.9) | 92.2 (89.4, 94.2) | 0.74 (0.44, 1.22) |
| Asia Pacific, East Europe, and South America | 20/414 (4.8) | 40/411 (9.7) | 94.0 (90.9, 96.1) | 89.4 (85.9, 92.1) | 0.50 (0.29, 0.85) |
HR=hazard ratio
Adapted from FDA review
What are the possible side effects?
NERLYNX may cause serious side effects, including severe diarrhea and liver damage.
The most common side effects that occurred in 15% of patients or more include diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, tiredness, vomiting and rash.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Table 4 below summarizes common adverse reactions at all grades of severity. This was based on safety population defined as all patients who received at least 1 dose of trial drug.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions reported in ≥ 2% of NERLYX Treated Patients in Trial 1
| System Organ Class (Preferred Term) | NERLYNX n=1408 | Placebo n=1408 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 (%) | Grade 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 (%) | Grade 4 (%) | ||
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | |||||||
| Diarrhea | 95 | 40 | 0.1 | 35 | 2 | 0 | |
| Nausea | 43 | 2 | 0 | 22 | 0.1 | 0 | |
| Abdominal pain1 | 36 | 2 | 0 | 15 | 0.4 | 0 | |
| Vomiting | 26 | 3 | 0 | 8 | 0.4 | 0 | |
| Stomatitis2 | 14 | 0.6 | 0 | 6 | 0.1 | 0 | |
| Dyspepsia | 10 | 0.4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| Abdominal distension | 5 | 0.3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dry mouth | 3 | 0.1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | |||||||
| Fatigue | 27 | 2 | 0 | 20 | 0.4 | 0 | |
| Hepatobiliary Disorders | |||||||
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 9 | 1 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.2 | 0 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 7 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.3 | 0 | |
| Infections and Infestations | |||||||
| Urinary tract infection | 5 | 0.1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Investigations | |||||||
| Weight decreased | 5 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | |||||||
| Decreased appetite | 12 | 0.2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dehydration | 4 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0 | |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | |||||||
| Muscle spasms | 11 | 0.1 | 0 | 3 | 0.1 | 0 | |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | |||||||
| Epistaxis | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.1 | 0 | |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | |||||||
| Rash3 | 18 | 0.6 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dry skin | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Nail Disorder4 | 8 | 0.3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Skin fissures | 2 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | |
1 Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal pain lower.
2 Includes stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, mouth ulceration, oral mucosal blistering, mucosal inflammation, oropharyngeal pain, oral pain, glossodynia, glossitis, and cheilitis.
3 Includes rash, rash erythematous, rash follicular, rash generalized, rash pruritic, rash pustular, rash maculo- papular, rash papular, dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, and toxic skin eruption.
4 Includes nail disorder, paronychia, onychoclasis, nail discoloration, nail toxicity, nail growth abnormal, and nail dystrophy.
NERLYNX Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The trial included only women therefore sex differences cannot be determined.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of overall side effects was similar in patients 65 years and below and those above 65 years. Certain side effects—called serious adverse events1—were seen more frequently in patients above 65 years. The serious adverse events most frequently reported in this age group were vomiting, diarrhea, kidney failure, and dehydration.
1 Serious adverse event was defined as any event that resulted in one of the following: death, life-threatening event, required hospitalization or extended a current hospital stay, persistent or significant disability/incapacity, cancer, or congenital anomaly or birth defect.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Analysis of side effects by subgroup was limited to age and race due to the fact that all patients in the trial were women.
Table 5. Summary of Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events (TEAEs) by Age
| NERLYNX N=1408 | Placebo N=1408 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65y> N=1236 | ≥65y N=172 | 65y> N=1235 | ≥65y N=173 | |
| Any TEAEs, n (%) | 1218 (99) | 169 (98) | 1085 (88) | 155 (90) |
| Grade 3 or 4, n (%) | 611 (49) | 89 (52) | 156 (13) | 28 (16) |
| SAEs, n (%) | 86 (7%) | 17 (10%) | 71 (6) | 14 (8) |
Table 6. Summary of Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events (TEAEs) by Race
| NERLYNIX N=1408 | Placebo N=1408 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White N=1156 | Asian N=188 | Black or AA N=25 | Other N=39 | White N=1125 | Asian N=197 | Black or AA N=45 | Other N=41 | |
| Any TEAEs, n (%) | 1137 (98) | 186 (99) | 25 (100) | 39 (100) | 991 (88) | 174 (88) | 37 (82) | 38 (93) |
| Grade 3 or 4, n (%) | 575 (50) | 96 (51) | 11 (44) | 18 (46) | 158 (14) | 13 (7) | 8 (18) | 5 (12) |
| SAEs, n (%) | 89 (8) | 10 (5) | 2 (8) | 2 (5) | 71 (6) | 8 (4) | 1 (2) | 5 (12) |
SAEs=serious adverse events
FDA review and Clinical Trial Report
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved NERLYNX based on evidence from a clinical trial of 2840 women with HER2-positive, early stage breast cancer who had been previously treated for breast cancer. The trial was conducted in Europe, North America, Asia, South America and Australia.
Figure 1 summarizes how many women were in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
FDA Review
Figure 2 and Table 1 summarize patients by race in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Table 1. Demographics by Race
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 2300 | 81 |
| Asian | 385 | 13 |
| Black or African American | 74 | 3 |
| Other | 81 | 3 |
FDA Review
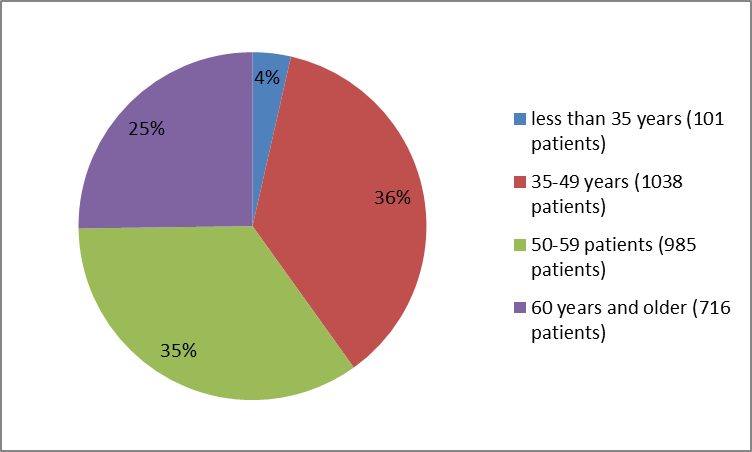
Figure 3 summarizes patients by age in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
The demographic characteristics of randomized population are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6. Baseline Demographic Characteristics
| NERLYNX (n=1420) | Placebo (n=1420) | Total (n=2840) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Women | 1420 (100.0) | 1420 (100.0) | 2840 (100.0) |
| Men | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 1165 (82.0) | 1135 (79.9) | 2300 (81.0) |
| Asian | 188 (13.2) | 197 (13.9) | 385 (13.6) |
| Black or African American | 27 (1.9) | 47 (3.3) | 74 (2.6) |
| Other | 40 (2.8) | 41 (2.9) | 81 (2.9) |
| Age (years) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 52.31 (10.08) | 52.27 (10.28) | 52.29 (10.18) |
| Median | 52.00 | 52.00 | 52.00 |
| Min, Max | 25, 83 | 23, 82 | 23, 83 |
| Age Group, n (%) | |||
| 35=""> | 46 (3.2) | 55 (3.9) | 101 (3.6) |
| 35-49 years | 523 (36.8) | 515 (36.3) | 1038 (36.5) |
| 50-59 years | 497 (35.0) | 488 (34.4) | 985 (34.7) |
| ≥ 60 years | 354 (24.9) | 362 (25.5) | 716 (25.2) |
| 65=""> | 1247 (87.8) | 1245 (87.8) | 2492 (87.7) |
| ≥ 65 years | 173 (12.2) | 175 (12.3) | 348 (12.3) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 23 (1.6) | 29 (2) | 52 (1.8) |
| Missing | 1397 (98.4) | 1391 (98) | 2788 (98.2) |
| Region, n (%) | |||
| North America | 519 (36.5) | 477 (33.6) | 996 (35.1) |
| Western Europe, Australia, and South Africa | 487 (34.3) | 532 (37.5) | 1019 (35.9) |
| Asia Pacific, East Europe, and South America | 414 (29.2) | 411 (28.9) | 825 (29.0) |
Adapted from FDA Review and Clinical Trial Report
How were the trials designed?
There was one trial that enrolled women with HER2-positive, early stage breast cancer who have been treated within 2 years with the medicine trastuzumab.
The trial compared patients who were randomly assigned to take either NERLYX or placebo tablets once a day. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until the trials were completed. The treatment continued until the disease returned, the side effects became too toxic, or the patients decided they no longer wanted to participate in the trial.
The trial measured the duration of time in each group before the women’s cancers returned or death occurred.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy efficacy of NERLYNX were evaluated in one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial. All patients were women with an early stage HER2-positive breast cancer, within two years of completing treatment with adjuvant trastuzumab.
The primary efficacy outcome measure of the trial was invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) defined as the time between the date of randomization to the first occurrence of invasive recurrence (local/regional, ipsilateral or contralateral breast cancer), distant recurrence, or death from any cause, with 2 years and 28 days of follow-up.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION