Drug Trials Snapshots: RETEVMO
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to RETEVMO Prescribing Information for complete information.
RETEVMO (selpercatinib)
reh-TEHV-moh
Eli Lilly and Company
Approval date: May 8, 2020
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
RETEVMO is a drug used to treat certain cancers caused by abnormal RET (rearranged during transfection) genes in:
- adult patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) which has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic).
- adults and children 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer (MTC).
- adults and children 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic thyroid cancer who have received radioactive iodine that did not work or is no longer working.
How is this drug used?
RETEVMO is a capsule usually taken by mouth twice a day.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Sixty-four percent of the 105 patients with previously treated NSCLC, experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than 6 months for 81% of them. Out of 39 patients who had never undergone treatment, 84% experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than 6 months for 58% of them.
Sixty-nine percent of the 55 previously treated patients for MTC experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than 6 months for 76% of them. Out of 88 patients who had never undergone treatment with an approved drug, 73% experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than 6 months for 61% of them.
Seventy-nine percent of the 19 previously treated patients with thyroid cancer experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than 6 months for 87% of them. All eight patients who had not received therapy other than radioactive iodine therapy experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than 6 months for 75 % of them.
RETEVMO was approved under FDA’s accelerated approval program, which provides earlier patient access to a promising new drug while the company continues to conduct clinical trials to confirm that the drug works well.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The tables below summarize efficacy results for each indication based on overall response rate as determined by a Blinded Independent Review Committee (BIRC) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1. An additional efficacy outcome measure was duration of response (DOR) by BIRC.
Table 1. Efficacy Results for Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC Previously Treated with Platinum Chemotherapy
| RETEVMO (n = 105) |
|
|---|---|
| Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) | 64% (54%, 73%) |
| Complete response | 1.9% |
| Partial response | 62% |
| Duration of Response | |
| Median in months (95% CI) | 17.5 (12, NE) |
| % with >6 months2 | 81 |
Table 2. Efficacy Results in Treatment-Naïve Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC
| RETEVMO (n = 39) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) | 85% (70%, 94%) | |
| Complete response | 0 | |
| Partial response | 85% | |
| Duration of Response | ||
| Median in months (95% CI) | NE (12, NE) | |
| % with >6 months2 | 58 | |
Table 3. Efficacy Results in RET-Mutant MTC Previously Treated with Cabozantinib or Vandetanib
| RETEVMO (n = 55) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) | 69% (55%, 81%) | |
| Complete response | 9% | |
| Partial response | 60% | |
| Duration of Response | ||
| Median in months (95% CI) | NE (19.1, NE) | |
| % with >6 months2 | 76 | |
Table 4. Efficacy Results in Cabozantinib and Vandetanib-naïve RET-Mutant MTC
| RETEVMO (n = 88) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) | 73% (62%, 82%) | |
| Complete response | 11% | |
| Partial response | 61% | |
| Duration of Response | ||
| Median in months (95% CI) | 22.0 (NE, NE) | |
| % with >6 months2 | 61 | |
Table 5. Efficacy Results RET Fusion-Positive Thyroid Cancer
| RETEVMO Previously Treated (n = 19) |
RETEVMO Systemic Therapy Naïve (n = 8) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) | 79% (54%, 94%) | 100% (63%, 100%) |
| Complete response | 5.3% | 12.5% |
| Partial response | 74% | 88% |
| Duration of Response | ||
| Median in months (95% CI) | 18.4 (7.6, NE) | NE (NE, NE) |
| % with >6 months2 | 87 | 75 |
1Confirmed overall response rate assessed by BICR.
2 Based on observed duration of response
NE = not estimable
RETEVMO Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: RETEVMO worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: RETEVMO worked similarly in White and Asian patients. Differences among other races could not be determined because of the small number of patients of other races.
- Age: RETEVMO worked similarly in patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize overall response rate and duration of response by sex, race and age subgroups. Results should be interpreted with caution given the small sample size overall, and the limited number of patients in each subgroup.
Table 6. Subgroup Analyses for Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC Previously Treated with Platinum Chemotherapy
| Previously Treated Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Responders | ORR, % (95% CI) |
DOR, months (Range) | |
| Overall | 105 | 67 | 63.8 (53.9, 73.0) |
17.51 (1.9+, 26.2+) |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 43 | 23 | 53.5 (37.7, 68.8) |
12.45 (1.9+, 14.8+) |
| Female | 62 | 44 | 71.0 (58.1, 81.8) |
NR (1.9+, 26.2+) |
| Race | ||||
| White | 55 | 36 | 65.5 (51.4, 77.8) |
17.51 (1.9+, 26.2+) |
| Asian | 40 | 24 | 60.0 (43.3, 75.1) |
NR (1.9+, 14.8+) |
| Other | 10 | 7 | 70.0 (34.8, 93.3) |
14.65 (3.5, 14.8+) |
| Age | ||||
| < 65 years | 69 | 46 | 66.7 (54.3, 77.6) |
17.51 (1.9+, 26.2+) |
| ≥ 65 years | 36 | 21 | 58.3 (40.8, 74.5) |
14.65 (4.7, 24.0+) |
Table 7. Subgroup Analyses for Metastatic RET Mutant MTC
| Previously Treated with Cabozantinib or Vandetanib | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Responders | ORR, % (95% CI) |
DOR, months (Range) | |
| Overall | 55 | 38 | 69.1 (55.2, 80.9) |
NR (2.8+, 23.1+) |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 36 | 25 | 69.4 (51.9,83.7) |
NR (2.8+, 24.0+) |
| Female | 19 | 13 | 68.4 (43.5, 87.4) |
19.1 (2.8+, 19.1) |
| Race | ||||
| White | 49 | 34 | 69.4 (54.6, 81.8) |
NR (2.8+, 24.0+) |
| Other | 6 | 4 | 66.7 (22.3, 95.7) |
NR (2.8+, 23.0+) |
| Age | ||||
| < 65 years | 37 | 25 | 67.6 (50.2, 82.0) |
NR (2.8+, 24.0+) |
| ≥ 65 years | 18 | 13 | 72.2 (46.5, 90.3) |
NR (3.5+, 17.5+) |
CI = confidence interval
Adapted from FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
RETEVMO may cause serious side effects including liver toxicity, high blood pressure, heart rhythm changes due to prolongation of heart electrical activity (QT prolongation), bleeding, allergic reactions, impaired wound healing and harm to an unborn baby.
The most common side effects of RETEVMO are changes in laboratory tests (including increased liver enzymes, increased blood sugar, decreased white cell and platelet counts, decreased protein level, decreased calcium, increased total cholesterol, increased creatinine, and decreased sodium) dry mouth, diarrhea, high blood pressure, fatigue, edema, rash, and constipation.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The tables below summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalitiest that occurred in patients treated with RETEVMO at 160 mg orally twice daily.
Table 8. Adverse Reactions (≥ 15%) in Patients Who Received RETEVMO
| Adverse Reaction | RETEVMO (n = 702) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Grades 1-4 (%) |
Grades 3-4 (%) |
|
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Dry Mouth | 39 | 0 |
| Diarrhea1 | 37 | 3.4* |
| Constipation | 25 | 0.6* |
| Nausea | 23 | 0.6* |
| Abdominal pain2 | 23 | 1.9* |
| Vomiting | 15 | 0.3* |
| Vascular | ||
| Hypertension | 35 | 18 |
| General | ||
| Fatigue3 | 35 | 2* |
| Edema4 | 33 | 0.3* |
| Skin | ||
| Rash5 | 27 | 0.7* |
| Nervous System | ||
| Headache6 | 23 | 1.4* |
| Respiratory | ||
| Cough7 | 18 | 0 |
| Dyspnea8 | 16 | 2.3 |
| Investigations | ||
| Prolonged QT interval | 17 | 4* |
| Blood and Lymphatic System | ||
| Hemorrhage9 | 15 | 1.9 |
1Diarrhea includes diarrhea, defecation urgency, frequent bowel movements, and anal incontinence
2Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, abdominal discomfort, gastrointestinal pain
3Fatigue includes fatigue, asthenia, malaise.
4Edema includes edema, edema peripheral, face edema, eye edema, eyelid edema, generalized edema, localized edema, lymph edema, scrotal edema, peripheral swelling, scrotal swelling, swelling, swelling face, eye swelling, peripheral swelling
5Includes rash, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash maculopapular, rash morbilliform, rash pruritic
6Headache includes headache, sinus headache, tension headache
7Includes cough, productive cough
8Includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, dyspnea at rest
9Hemorrhage includes epistaxis, hematuria, hemoptysis, contusion, rectal hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, ecchymosis, hematochezia, petechiae, traumatic hematoma, anal hemorrhage, blood blister, blood urine present, cerebral hemorrhage, gastric hemorrhage, hemorrhage intracranial, spontaneous hematoma, abdominal wall hematoma, angina bullosa hemorrhagica, diverticulum intestinal hemorrhagic, eye hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gingival bleeding, hematemesis, hemorrhagic anemia, intraabdominal hemorrhage, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, melena, mouth hemorrhage, occult blood positive, pelvic hematoma, periorbital hematoma, pharyngeal hemorrhage, pulmonary contusion, purpura, retroperitoneal hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, vessel puncture site hematoma
*Only includes a grade 3 adverse reaction.
Table 9. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 20%) Worsening from Baseline in Patients Who Received RETEVMO
| Laboratory Abnormality | RETEVMO1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Grades 1-4 (%) |
Grades 3-4 (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased AST | 51 | 8 |
| Increased ALT | 45 | 9 |
| Increased glucose | 44 | 2.2 |
| Decreased albumin | 42 | 0.7 |
| Decreased calcium | 41 | 3.8 |
| Increased creatinine | 37 | 1.0 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 36 | 2.3 |
| Increased total cholesterol | 31 | 0.1 |
| Decreased sodium | 27 | 7 |
| Decreased magnesium | 24 | 0.6 |
| Increased potassium | 24 | 1.2 |
| Increased bilirubin | 23 | 2.0 |
| Decreased glucose | 22 | 0.7 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased leukocytes | 43 | 1.6 |
| Decreased platelets | 33 | 2.7 |
1Denominator for each laboratory parameter is based on the number of patients with a baseline and post-treatment laboratory value available, which ranged from 675 to 692 patients.
RETEVMO Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar between White and Asian patients. Differences in side effects among other races could not be determined because of the small number of patients of other races.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar between patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Tables 10-12 summarize adverse events that occurred in sex, race and age subgroups.
Table 10. Subgroup Analysis of Adverse Events by Sex (safety population)
| Male (N=368) |
Female (N=334) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Patients with TEAEs | 365 (99.2) | 330 (98.8) |
| Patients with TEAEs Maximum Severity >= 3 | 205 (55.7) | 210 (62.9) |
| Patients with Serious TEAEs | 122 (33.2) | 112 (33.5) |
| Patients with Fatal TEAEs | 13 (3.5) | 8 (2.4) |
Table 11. Subgroup Analysis of Adverse Events by Race (safety population)
| White (N=485) |
Asian (N=154) |
All Others (N=63) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with TEAEs | 482 (99.4) | 151 (98.1) | 62 (99.0) |
| Patients with TEAEs Maximum Severity >= 3 | 290 (59.8) | 87 (56.5) | 38 (60.3) |
| Patients with Serious TEAEs | 170 (35.1) | 43 (27.9) | 21 (33.3) |
| Patients with Fatal TEAEs | 13 (12.7) | 6 (3.9) | 2 (3.2) |
Table 12. Subgroup Analysis of Adverse Events by Age (safety population)
| < 65 years (N=463) |
≥65 Years (N=239) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Patients with TEAEs | 458 (98.9) | 237 (99.2) |
| Patients with TEAEs Maximum Severity >= 3 | 259 (55.9) | 156 (65.3) |
| Patients with Serious TEAEs | 131 (28.3) | 103 (43.1) |
| Patients with Fatal TEAEs | 11 (2.4) | 10 (4.2) |
TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event
FDA Review
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the trials?
The FDA approved RETEVMO based on the evidence from one clinical trial (NCT03157128) of 702 patients 15-92 years old with certain cancers caused by abnormal RET genes. The trial was conducted at 84 sites in the United States, Canada, Australia, Hong Kong, Japan, South Korea, Singapore,Taiwan, Switzerland, Germany, Denmark, Spain, France, United Kingdom, Italy and Israel.
All 702 patients that provided data for the assessment of side effects of RETEVMO (safety population) are presented below. Some of these patients provided data for the assessment of the benefits of RETEVMO for NSCLC, some for benefits for MTC and some for benefits for thyroid cancer. Demographic data of these patients that formed efficacy populations are presented in Tables 14 and 15 under MORE INFO 5.
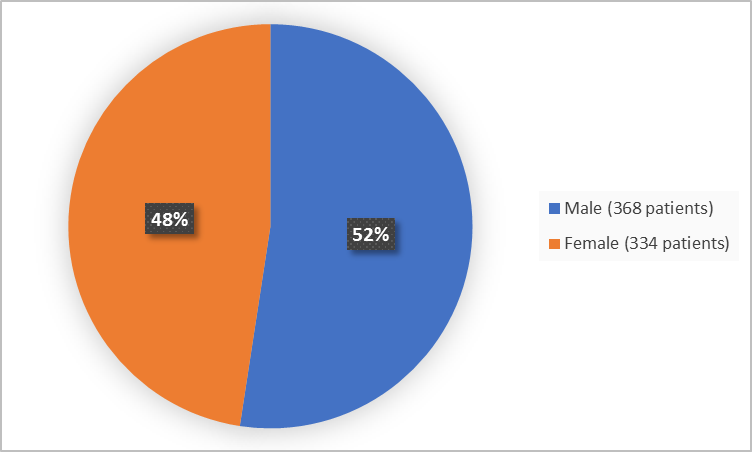
Figure 1 below summarizes by sex how many patients were in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Demographics by Sex (safety population)
Adapted from FDA Review
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients in the clinical trial by race.
Figure 2. Demographics by Race (safety population)
*includes American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander Other, and Unknown
Adapted from FDA Review
Figure 3 below summarizes the percentage of patients in the clinical trial by age.
Figure 3. Demographics by Age (safety population)
Adapted from FDA Review
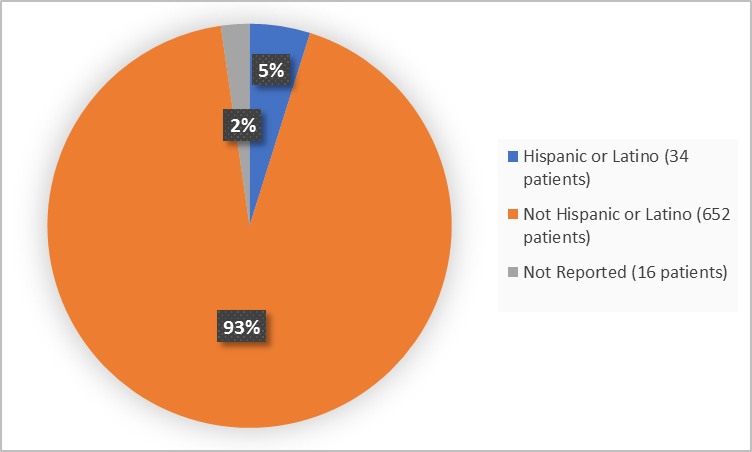
Figure 4. Demographics by Ethnicity (safety population)
Adapted from FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
Table 13 below summarizes demographics for the patients who received at least one dose of RETEVMO (safety population). Efficacy populations are presented in Tables 14 and 15.
Table 13. Demographics of Patients in the Clinical Trial (safety population)
| Demographic Parameter | RETEVMO | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RET-mutant MTC N=299 |
RET Fusion-positive NSCLC N=329 |
Overall N=702 |
|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 184 (61.5) | 144 (43.8) | 368 (52.4) |
| Female | 115 (38.7) | 185 (56.2) | 334 (47.6) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 262 (87.6) | 165 (50.2) | 485 (69.1) |
| Asian | 12 (4.0) | 136 (41.3) | 154 (21.9) |
| Black or African American | 4 (1.3) | 16 (4.9) | 24 (3.4) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.3) |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 1 (0.3) | 0 | 2 (0.3) |
| Other/ Unknown | 19 (6.4) | 11 (3.3) | 35 (5.0) |
| Age, years | |||
| Mean (SD) | 55.9 | 59.4 | 57.5 |
| Median | 58.0 | 61.0 | 59.0 |
| Range | 15, 90 | 23, 92 | 15, 92 |
| Age group, n (%) | |||
| < 18 years | 3 (1.0) | 0 | 3 (0.4) |
| 18–44 years | 67 (22.4) | 39 (11.9) | 123 (17.5) |
| 45–64 years | 136 (45.5) | 169 (51.4) | 337 (48.0) |
| 65–74 years | 61 (20.4) | 96 (29.2) | 172 (24.5) |
| ≥ 75 years | 32 (10.7) | 25 (7.6) | 67 (9.5) |
| Ethnicity, n(%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 17 (5.7) | 9 (2.7) | 34 (4.8) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 275 (92) | 315 (95.7) | 652 (92.9) |
| Not Reported | 7 (2.3) | 5 (1.5) | 16 (2.3) |
| Region, n(%) | |||
| US | 203 (67.9) | 165 (50.2) | 427 (60.8) |
| All Other | 96 (32.1) | 164 (49.8) | 275 (39.2) |
Adapted from FDA Review
Table 14. Efficacy Populations for Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC and RET Fusion-Positive Thyroid Cancer
| Demographic Parameter | RET Fusion-positive NSCLC | RET fusion-positive Thyroid Ca N = 27 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Previously Treated N = 105 | Treatment-naïve N = 39 |
||
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 43 (41.0) | 17 (43.6) | 14 (51.9) |
| Female | 62 (59.0) | 22 (56.4) | 13 (48.1) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 55 (52.4) | 28 (71.8) | 20 (74.1) |
| Black or African American | 5 (4.8) | 3 (7.7) | 1 (3.7) |
| Asian | 40 (38.1) | 7 (17.9) | 2 (7.4) |
| Other/Missing | 5 (4.8) | 1 (2.6) | 4 (14.8) |
| Age, years | |||
| Median | 61.0 | 61.0 | 54.0 |
| Range | 23-81 | 23-86 | 20-88 |
| Age group, n (%) | |||
| 18-44 years | 17 (16.2) | 4 (10.3) | 7 (25.9) |
| 45-64 years | 52 (49.5) | 18 (46.2) | 11 (40.7) |
| 65-74 years | 30 (28.6) | 13 (33.3) | 5 (18.5) |
| ≥ 75 years | 6 (5.7) | 4 (10.3) | 4 (14.8) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 4 (3.8) | 0 | 3 (11.1) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 98 (93.3) | 38 (97.4) | 22 (81.5) |
| Missing | 3 (2.9) | 1 (2.6) | 2 (7.4) |
Table 15. Efficacy Population for RET-Mutant MTC
| Demographic Parameter | RET-mutant MTC | |
|---|---|---|
| Previously Treated with Cabozantinib or Vandetanib N = 55 |
Treatment naïve N = 88 |
|
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 36 (65.6) | 58 (65.9) |
| Female | 19 (34.5) | 30 (34.1) |
| Race, n (%) | ||
| White | 49 (89.1) | 75 (85.2) |
| Black or African American | 1 (1.8) | 1 (1.1) |
| Asian | 0 | 4 (4.5) |
| Other/Missing | 5 (9.1) | 8 (9.1) |
| Age, years | ||
| Median | 57.0 | 58.0 |
| Range | 17-84 | 15-82 |
| Age Group, n (%) | ||
| <18 years | 1 (1.8) | 2 (2.3) |
| 18–44 years | 9 (16.4) | 20 (22.7) |
| 45–64 years | 27 (49.1) | 43 (48.9) |
| 65–74 years | 12 (21.8) | 14 (15.9) |
| ≥ 75 years | 6 (10.9) | 9 (10.2) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 4 (7.3) | 2 (2.3) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 50 (90.9) | 84 (95.5) |
| Missing | 1 (1.8) | 2 (2.3) |
Adapted from FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
The benefits and side effects of RETEVMO for certain cancers caused by abnormal RET genes were evaluated in one clinical trial. Some patients were previously treated for their cancer and some were not (treatment-naïve). All patients received RETEVMO by mouth twice a day until either cancer progression or intolerable side effects.
The benefit of RETEVMO was evaluated by measuring the percentage of patients who achieved complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors (overall response rate or ORR) and by measuring the duration of that benefit (duration of response or DoR).
How were the trials designed?
There was one multicenter, open-label, multi-cohort trial that provided data to evaluate safety and the efficacy of RETEVMO for patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive cancer.
The efficacy of RETEVMO for metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC was evaluated in adult patients previously treated with platinum chemotherapy and in treatment-naïve patients.
The efficacy of RETEVMO for advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC was evaluated in patients who had been previously treated with cabozantinib, vandetanib or both, and patients who had not received prior treatment with cabozantinib or vandetanib.
The efficacy for RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer was evaluated in adults and pediatric patients who were radioactive iodine-refractory (RAI, if an appropriate treatment option) and had received another prior systemic treatment, and in patients with RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer who were RAI-refractory and had not received any additional therapy.
Patients received RETEVMO orally twice daily until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. The major efficacy outcome measure for all cohorts was overall response rate and additional measure was duration of response as determined by a blinded independent review committee according to RECIST v1.1.
Safety assessment was done on all patients who received at least one dose of RETEVMO.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION