Drug Trial Snapshot: BRAFTOVI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
BRAFTOVI is a drug which is to be used with another drug, binimetinib, to treat a type of skin cancer called melanoma. The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the BRAFTOVI Prescribing Information for complete information.
BRAFTOVI (encorafenib)
(braf-TOE-vee)
Array Biopharma
Approval date: June 27, 2018
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
BRAFTOVI is a drug which is to be used with another drug, binimetinib, to treat a type of skin cancer called melanoma. BRAFTOVI is only to be used in patients who have melanoma with a specific abnormal gene (called a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation) that has spread to other parts of the body (advanced melanoma) or cannot be removed by surgery.
How is this drug used?
BRAFTOVI is a tablet. A total of 450 mg is taken by mouth once daily with binimetinib.
What are the benefits of this drug?
BRAFTOVI plus binimetinib delays disease worsening. In addition, 63% of patients taking BRAFTOVI plus binimetinib experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The table below summarizes efficacy results for the clinical trial. The major efficacy outcome was progression-free survival (PFS) per RECIST v1.1 as assessed by blinded independent central review.
Table 2. Efficacy Results from the Clinical Trial
|
|
BRAFTOVI |
Vemurafenib |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Progression-Free Survivala |
||||
|
Number of Events (%) |
98 (51) |
106 (55) |
||
|
Progressive Disease |
88 (46) |
104 (54) |
||
|
Death |
10 (5) |
2 (1) |
||
|
Median PFS in months (95% CI) |
14.9 (11, 18.5) |
7.3 (5.6, 8.2) |
||
|
HR (95% CI)b |
0.54 (0.41, 0.71) |
|||
|
P valuec |
<> |
|||
|
Overall Response Rate |
||||
|
ORR (95% CI) |
63% (56%, 70%) |
40% (33%, 48%) |
||
|
CR |
8% |
6% |
||
|
PR |
55% |
35% |
||
|
Duration of Response |
|
|
||
|
Median DoR months (95% CI) |
16.6 (12.2, 20.4) |
12.3 (6.9, 16.9) |
||
CI = Confidence interval; CR = Complete response; HR = Hazard ratio; NE = Not estimable; PFS = Progression-free survival; PR = Partial response.
a Estimated with Cox proportional hazard model adjusted by the following stratification factors: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Stage (IIIB, IIIC, IVM1a or IVM1b, versus IVM1c) and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (0 versus 1).
b Log-rank test adjusted by the same stratification factors.
BRAFTOVI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: BRAFTOVI worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in how well the drug worked among races could not be determined.
- Age: BRAFTOVI worked similarly in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes efficacy results by subgroup.
Table 3. Progression-Free Survival Results in Demographic Subgroups
|
Demographic Subgroup |
BRAFTOVI |
Vemurafenib |
HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Overall |
98/192 |
106/191 |
0.58 (0.44,0.77) |
|
Sex |
|||
|
Men |
63/115 |
61/111 |
0.62 (0.44, 0.89) |
|
Women |
35/77 |
45/80 |
0.5 (0.32, 0.79) |
|
Race |
|||
|
White |
93/181 |
91/166 |
0.59 (0.44, 0.79) |
|
All Other |
5/11 |
15/25 |
0.52 (0.19, 1.43) |
|
Age Category |
|||
|
<65> |
69/132 |
80/140 |
0.55 (0.4, 0.77) |
|
>=65 years |
29/60 |
26/51 |
0.66 (0.39, 1.12) |
HR=hazard ratio; CI=confidence interval
FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib may cause serious side effects including new skin cancers, bleeding, eye inflammation (uveitis) and heart rhythm problems (due to QT prolongation).
The most common side effects of treatment with BRAFTOVI when given with binimetinib are fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and joint pain.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse drug reactions in the clinical trial.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 10% of Patients Receiving BRAFTOVI in Combination with Binimetiniba
|
Adverse Reaction |
BRAFTOVI |
Vemurafenib |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All |
Grades |
All |
Grades |
|
|
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions |
||||
|
Fatiguec |
43 |
3 |
46 |
6 |
|
Pyrexiac |
18 |
4 |
30 |
0 |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders |
||||
|
Nausea |
41 |
2 |
34 |
2 |
|
Vomitingc |
30 |
2 |
16 |
1 |
|
Abdominal painc |
28 |
4 |
16 |
1 |
|
Constipation |
22 |
0 |
6 |
1 |
|
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders |
||||
|
Arthralgiac |
26 |
1 |
46 |
6 |
|
Myopathyc |
23 |
0 |
22 |
1 |
|
Pain in extremity |
11 |
1 |
13 |
1 |
|
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders |
||||
|
Hyperkeratosisc |
23 |
1 |
49 |
1 |
|
Rashc |
22 |
1 |
53 |
13 |
|
Dry skinc |
16 |
0 |
26 |
0 |
|
Alopeciac |
14 |
0 |
38 |
0 |
|
Pruritusc |
13 |
1 |
21 |
1 |
|
Nervous System Disorders |
||||
|
Headachec |
22 |
2 |
20 |
1 |
|
Dizzinessc |
15 |
3 |
4 |
0 |
|
Peripheral neuropathyc |
12 |
1 |
13 |
2 |
|
Vascular Disorders |
||||
|
Hemorrhagec |
19 |
3 |
9 |
2 |
aGrades per National Cancer Institute CTCAE v4.03.
bGrade 4 adverse reactions limited to fatigue (n=1), pruritus (n=1) and rash (n=1) in the BRAFTOVI plus binimetinib arm.
c Represents a composite of multiple, related preferred terms.
BRAFTOVI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Tables below summarize the incidence of treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) and serious adverse events (SAE) by sex and age subgroups.
Table 5. Per-patient Incidence of Adverse Events by Sex (Safety Population)
|
Event |
BRAFTOVI |
Vemurafenib |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Men |
Women |
Men |
Women |
|
|
Any TEAE |
112 (97.4) |
77 (100) |
107 99.1) |
78 (100) |
|
Grade 3-4 TEAE |
65 (56.6) |
46 (59.7) |
67 (62.0) |
51 (65.4) |
|
Any SAE |
42 (36.5) |
24 (31.2) |
41 (38.0) |
28 (35.9) |
|
Grade 3-4 SAE |
37 (32.3) |
20 (26.0) |
34 (31.5) |
26 (33.3) |
FDA Clinical Review
Table 6. Per-patient Incidence of Adverse Events by Age (Safety Population)
|
Event |
BRAFTOVI |
Vemurafenib |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
<65> |
≥65 years |
<65> |
≥65 years |
|
|
Any TEAE |
129 (97.7) |
60 (100) |
135 (99.3) |
50 (100) |
|
Grade 3-4 TEAE |
73 (55.3) |
38 (63.3) |
83 (61.0) |
35 (70) |
|
Any SAE |
42 (31.9) |
24 (40.0) |
53 (39.0) |
16 (32.0) |
|
Grade 3-4 SAE |
36 (27.3) |
21 (35.0) |
46 (33.8) |
14 (28.0) |
Adapted from FDA Review
WHO WAS IN THE STUDIES?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved BRAFTOVI based primarily on evidence from one clinical trial (NCT01909453) of 383 patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma that was advanced or could not be removed by surgery. The trial was conducted at 162 sites in Europe, North America and various countries around the world.
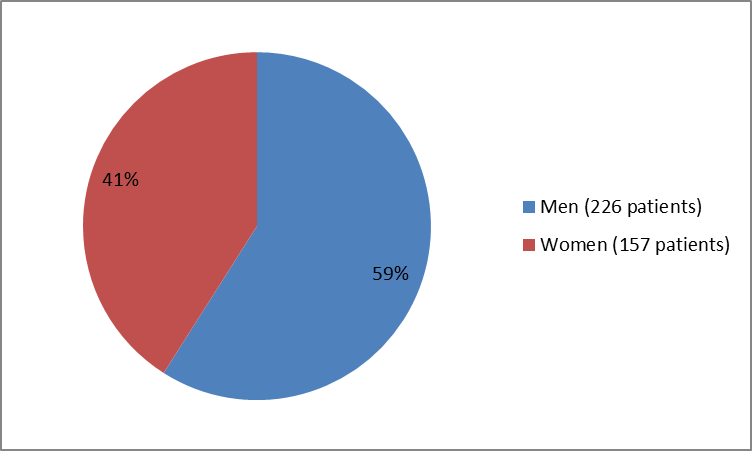
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Clinical Trial Data
Figure 2 and Table 1 summarize the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Clinical Trial Data
Table 1. Baseline Demographics by Race
|
Race |
Number of Patients |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|
|
White |
348 |
91 |
|
Asian |
13 |
3 |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
2 |
0.5 |
|
Other |
5 |
1 |
|
Unknown |
13 |
3 |
|
Missing data |
2 |
0.5 |
The figure below summarizes the percentage of patients by age in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Clinical Trial Data
The table below summarizes baseline demographics for patients in the trial.
Table 7. Baseline Demographics for the Clinical Trial
|
Demographic Category |
BRAFTOVI with binimetinib |
Vemurafenib |
TOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sex, n(%) |
|||
|
Men |
115 (60) |
111 (58) |
226 (59) |
|
Women |
77 (40) |
80 (42) |
157 (41) |
|
Race, n(%) |
|||
|
White |
181 (94) |
167 (87) |
348 (91) |
|
Asian |
5 (3) |
8 (4) |
13 (3) |
|
American Indian or Alaska |
0 (0) |
2 (1) |
2 (0.5) |
|
Other |
3 (2) |
2 (1) |
5 (1) |
|
Unknown |
2 (1) |
11 (6) |
13 (3) |
|
Missing |
1 (1) |
1 (1) |
2 (0.5)) |
|
Age Category, n(%) |
|||
|
<65> |
132 (69) |
140 (73) |
272 (71) |
|
>=65 years |
60 (31) |
51 (27) |
111 (29) |
|
Ethnicity, n(%) |
|||
|
Hispanic or Latino |
20 (10) |
14 (7) |
34 (9) |
|
Not Hispanic or Latino |
|
|
291 (88) |
|
Unknown |
17 (9) |
26 (14) |
43 (11) |
|
Missing |
6 (3) |
9 (5) |
15 (4) |
|
Region, n(%) |
|||
|
North America |
17 (9) |
17 (9) |
34 (9) |
|
Europe |
156 (81) |
153 (81) |
309 (81) |
|
Australia |
5 (3) |
6 (3) |
11 (3) |
|
Other |
14 (7) |
15 (7) |
29 (7) |
Clinical Trial Date
How were the trials designed?
The benefits and side effects of BRAFTOVI were evaluated in one clinical trial. Enrolled patients had a melanoma with a certain type of abnormal gene (called BRAF V600E or V600K mutation) that had spread to other parts of the body or that could not be removed by surgery.
All patients received daily either BRAFTOVI together with binimetinib or vemurafenib (FDA approved drug to treat melanoma). Both, patients and investigators knew which treatment had been given. Treatment continued until disease progression or development of unacceptable side effects.
The benefit of BRAFTOVI was assessed by measuring the length of time it took the disease to worsen in patients who received BRAFTOVI given with binimetinib and comparing it to the time the disease took to worsen in patients treated with vemurafenib.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of BRAFTOVI was established in a multicenter, randomized, open-label, active-controlled trial conducted in patients with BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive, unresectable or metastatic melanoma. The presence of mutation was detected using an FDA-approved mutation test.
Patients received BRAFTOVI once daily plus binimetinib twice daily or vemurafenib 960 mg twice daily. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome was progression-free survival (PFS) per RECIST v1.1 as assessed by blinded independent central review. Additional efficacy outcomes were investigator-assessed confirmed overall survival, objective response rate, and duration of response.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.