Drug Trial Snapshot: EMPAVELI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the EMPAVELI Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
EMPAVELI (pegcetacoplan)
(Em-puh-vel-ee )
Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Approval date: May 14, 2021
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
EMPAVELI is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with a disease called paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
PNH is a serious, life-threatening disease which is characterized by destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis), blood clots (thrombosis), and bone marrow dysfunction due to the overactivation of the complement system, a part of the body’s immune system.
How is this drug used?
EMPAVELI is given by infusion 2 times each week under the skin (subcutaneously) into the stomach (abdomen), back of upper arms, hips, or thighs using an infusion pump.
How were the trials designed?
EMPAVELI was evaluated in one clinical trial of 80 adult patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). This one trial evaluated the benefit and side effects of EMPAVELI in patients with PNH. In this trial, patients were previously treated on a stable dose of eculizumab for at least 3 months. Patients received either EMPAVELI or eculizumab for sixteen weeks. The benefit of EMPAVELI in comparison to eculizumab was assessed by change from baseline in hemoglobin values over a 16-week period.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Patients treated with EMPAVELI achieved an increase in hemoglobin level by 2.37 g/dL compared with those patients treated with eculizumab (-1.47 g/dL).
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The efficacy of EMPAVELI was based on change from baseline to Week 16 in hemoglobin level. The adjusted mean change from baseline in hemoglobin level was 2.37 g/dL in the group of patients treated with EMPAVELI versus -1.47 g/dL in the group of patients treated with eculizumab (p<0.0001).
Table 1. Change from Baseline in Hemoglobin Level at Week 16, ITT Population
|
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
LSM CFB in Hb (g/dL)1 (95% CI) |
|
|
EMPAVELI, N=41 |
2.37 (1.63, 3.10) |
|
Eculizumab, N=39 |
-1.47 (-2.81, -0.13) |
|
Difference in LSM between EMPAVELI and eculizumab (95% CI) |
3.84 (2.33, 5.34) |
|
p-value for difference in LSM2 |
<0.0001 |
1 Endpoint values after transfusion and study withdrawal were set to missing.
2 P-value was based on a mixed model for repeated measures, which included the categorical effects of treatment, visit, treatment by visit interaction, and stratification factors (transfusion history and platelet count at screening), and the continuous covariate of baseline value.
Abbreviations: CFB, change from baseline; CI, confidence interval; Hb, hemoglobin; least squares mean; N, number of patients
Adapted from FDA Review
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: EMPAVELI worked similarly in males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in how EMPAVELI worked among races could not be determined.
- Age: The number of patients > 65years of age was small; therefore, differences in how well EMPAVELI worked between older adults and younger adults could not be determined.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Subgroup efficacy analyses were performed only on sex groups because most patients were White and between 18-64 years of age.
Table 2. Change from Baseline in Hemoglobin Level by Sex at Week 16, ITT Population
|
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Sex: female |
|
|
LSM CFB in Hb (g/dL)1 (95% CI) |
|
|
EMPAVELI, N=41, n=27 |
1.64 (0.50, 2.78) |
|
Eculizumab, N=39, n=22 |
-1.95 (-4.30, 0.40) |
|
Difference in LSM between EMPAVELI and eculizumab (95% CI) |
3.59 (1.00, 6.18) |
|
Sex: male |
|
|
LSM CFB in Hb (g/dL)1 (95% CI) |
|
|
EMPAVELI, N=41, n=14 |
3.87 (2.66, 5.09) |
|
Eculizumab, N=39, n=17 |
-0.93 (-2.45, 0.58) |
|
Difference in LSM between EMPAVELI and eculizumab (95% CI) |
4.80 (2.89, 6.72) |
1 Endpoint values after transfusion and study withdrawal were set to missing.
Results are based on a mixed model for repeated measures, which included the categorical effects of treatment, visit, treatment by visit interaction, and stratification factors (transfusion history and platelet count at screening), and the continuous covariate of baseline value.
Abbreviations: CFB, change from baseline; CI, confidence interval; Hb, hemoglobin; least squares mean; N, number of patients; n, number of patients with specified characteristic
Adapted from FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effects were injection-site reactions, infections, diarrhea, abdominal pain, respiratory tract infection, viral infection, and tiredness.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in the Trial APL2-302.
Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events Reported in ≥ 5% of Patients Treated With EMPAVELI
|
Adverse Reaction |
EMPAVELI |
Eculizumab |
|---|---|---|
|
General disorders and administration site conditions Injection site reaction* Fatigue* Chest pain* |
16 (39) 5 (12) 3 (7) |
2 (5.1) 9 (23.1) 1 (2.6) |
|
Infections* Respiratory tract infection* Viral infection |
12 (29) 6 (15) 5 (12) |
10 (25.6) 5 (12.8) 3 (7.7) |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders Diarrhea Abdominal pain* |
9 (22) 8 (20) |
1 (2.6) 4 (10.3) |
|
Nervous system disorders Headache |
3 (7) |
9 (23) |
|
Musculoskeletal disorders Back pain* |
3 (7) |
4 (10) |
|
Cardiovascular disorders Systemic hypertension* |
3 (7) |
1 (3) |
*The following terms were combined:
Abdominal pain includes: abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abdominal pain lower, abdominal tenderness, epigastric discomfort
Back pain includes: back pain, sciatica
Chest pain includes: chest discomfort, non-cardiac chest pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, chest pain
Fatigue includes: asthenia, lethargy, fatigue
Infections include: oral herpes, bacterial infection, fungal infection, gastrointestinal infection, gastrointestinal viral infection, influenza-like illness, nasopharyngitis, pulpitis dental, rhinitis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis bacterial, vulvovaginal mycotic infection, hordeolum, sepsis, furuncle, otitis externa, viral respiratory tract infection, gastroenteritis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, ear infection, respiratory tract infection, rhinovirus infection, sinusitis, urinary tract infection
Injection-site reaction includes: injection-site erythema, injection-site reaction, injection-site swelling, injection-site induration, injection-site bruising, injection-site pain, injection-site pruritus, vaccination-site reaction, administration-site swelling, injection-site hemorrhage, injection-site edema, injection-site warmth, administration-site pain, application-site pain, injection-site mass, injection-site rash, vaccination-site pain
Respiratory tract infection includes: influenza-like illness, nasopharyngitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis, viral upper respiratory tract infection, upper respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract infection, sinusitis
Systemic hypertension includes: hypertension
Viral infection includes: oral herpes, gastrointestinal viral infection, viral upper respiratory tract infection, rhinovirus
EMPAVELI may cause serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis types A, C, W, Y, and B, and Haemophilus influenza type B.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar between males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in the occurrences of side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The number of patients > 65 years of age was small; therefore, differences in the occurrences of side effects between older adults and younger adults could not be determined.
Demographics Snapshot
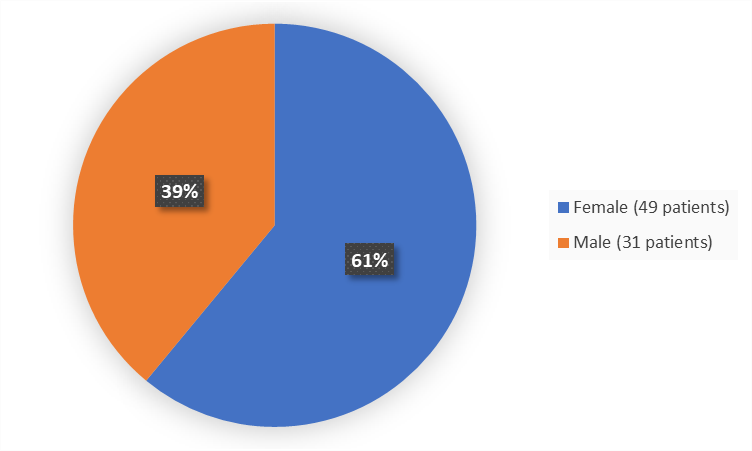
Sex
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the efficacy and safety of EMPAVELI.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (ITT Population)
Adapted from FDA review
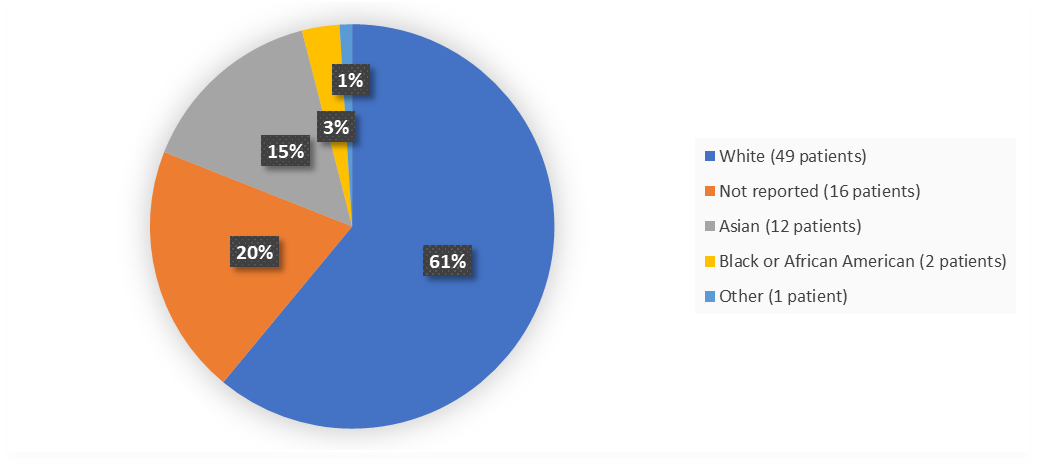
Race
Figure 2 summarizes the percent of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the efficacy and safety of EMPAVELI.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (ITT Population)
Adapted from FDA review
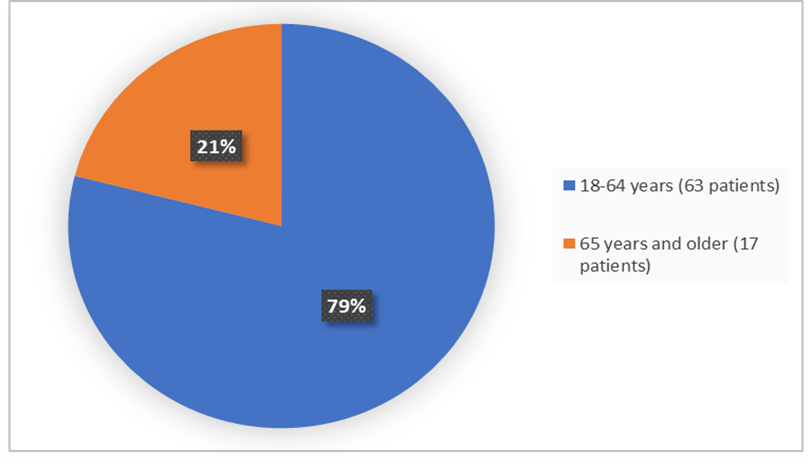
The figure below summarizes how many patients by age were in the trial used to evaluate the efficacy and safety of EMPAVELI.
Age
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age (ITT Population)
Adapted from FDA review
Table 8 summarizes the baseline demographics of the patients in the trial used to evaluate the efficacy and safety of EMPAVELI.
Table 8: Baseline Demographic Characteristics, ITT Population
|
Characteristic |
EMPAVELI |
Eculizumab |
|---|---|---|
|
Sex, n (%) Male Female |
14 (34.1) 27 (65.9) |
17 (43.6) 22 (56.4) |
|
Age, years Mean (SD) Median (min, max) |
50.2 (16.29) 53.0 (19, 81) |
47.3 (15.81) 47.0 (23, 78) |
|
Age ranges in years, n (%) ≥ 17 to <65 ≥ 65 to <75 ≥ 75 |
31 (75.6) 7 (17.1) 3 (7.3) |
32 (82.1) 6 (15.4) 1 (2.6) |
|
Race, n (%) White Asian Black/ African American Other Not reported |
24 (58.5) 5 (12.2) 2 (4.9) 0 10 (24.4) |
25 (64.1) 7 (17.9) 0 1 (2.6) 6 (15.4) |
|
Ethnicity, n (%) United States France Germany United Kingdom Japan Canada Australia Belgium Spain South Korea Russia |
7 (17.1) 10 (24.4) 7 (17.1) 6 (14.6) 5 (12.2) 3 (7.3) 1 (2.4) 1 (2.4) 1 (2.4) 0 0 |
7 (18.0) 6 (15.4) 4 (10.3) 5 (12.8) 5 (12.8) 1 (2.6) 4 (10.3) 3 (7.7) 1 (2.6) 1 (2.6) 2 (5.1) |
Adapted from FDA Review
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.