Drug Trials Snapshot: WELIREG
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the WELIREG Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
WELIREG (belzutifan)
(well-ih-reg)
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corporation
Original Approval date: August 13, 2021
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
WELIREG is a drug used for the treatment of adults with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease who require therapy for associated renal cell carcinoma, central nervous system hemangioblastomas, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, not requiring immediate surgery. VHL disease is a rare hereditary condition characterized by the formation of tumors and fluid-filled sacs (cysts) in many parts of the body.
How is this drug used?
WELIREG is a tablet taken by mouth once daily, with or without food.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved WELIREG based on evidence from a clinical trial of 61 patients with VHL associated renal cell carcinoma (RCC) diagnosed based on a VHL germline alteration and with at least one measurable solid tumor localized to the kidney. The trial was conducted at 11 sites in 4 countries in (Denmark, France, United Kingdom, and the United States). The same trial was used to assess efficacy and safety. In addition, a separate safety trial in patients with advanced VHL-associated renal cell carcinoma provided supportive safety data.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In the trial, approximately half of the 61 patients who received WELIREG had partial or complete shrinkage of their tumor which lasted an average of about a year.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Table 1. Benefits of WELIREG in VHL-Associated Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
Efficacy Outcome Measure |
WELIREG |
|---|---|
|
Overall response rate, % (n), [95% CI] |
49% (30)*, [36, 62] |
|
Complete response |
0% |
|
Partial response |
49% |
|
Duration of response |
|
|
Median in months (range) |
Not reached (2.8+, 22+) |
|
% (n) with duration of response ≥12 months |
56% (17/30) |
Source: WELIREG Prescribing Information
* All patients with a response were followed for a minimum of 18 months from the start of treatment.
+ Denotes ongoing response
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; VHL, von-Hippel Lindau disease
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: WELIREG worked similarly in males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in how well WELIREG worked in other races cannot be determined.
- Age: The number of patients 65 years of age and older was small; therefore, differences in how well WELIREG worked among age groups cannot be determined.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 2. Overall Response Rate Results by Sex
|
Efficacy Outcome Measure |
Males |
Females |
|---|---|---|
|
Overall response rate, % (n), [95% CI] |
44% (14), [26, 62] |
55% (16), [36, 74] |
|
Complete response |
0% |
0% |
|
Partial response |
44% |
55% |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval
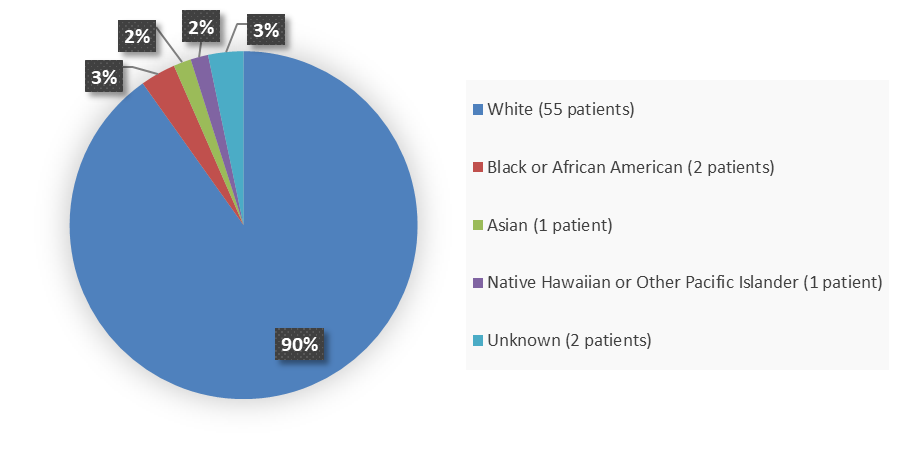
The study population include one Asian patient, 2 Black or African American patients, 1 Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, 55 White patients and 2 patients of unknown race
What are the possible side effects?
WELIREG can cause serious side effects, including anemia (low blood count) and hypoxia (low oxygen).
WELIREG can render some hormonal contraceptives ineffective, and exposure during pregnancy can harm an unborn baby.
The most common side effects were anemia, fatigue, impaired kidney function, headache, dizziness, high blood sugar, and nausea.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Table 3. Side Effects Occurring in ≥10% of Patients Who Received WELIREG in Study 004
|
Side Effect |
WELIREG |
|
|---|---|---|
|
All Grades |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|
|
Blood and lymphatic |
||
|
Anemia |
90 |
7 |
|
General |
||
|
Fatigue1 |
64 |
5 |
|
Nervous system |
||
|
Headache2 |
39 |
0 |
|
Dizziness3 |
38 |
0 |
|
Gastrointestinal |
||
|
Nausea |
31 |
0 |
|
Constipation |
13 |
0 |
|
Abdominal pain4 |
13 |
0 |
|
Eye disorders |
||
|
Visual impairment5 |
21 |
3.3 |
|
Infections |
||
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
21 |
0 |
|
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal |
||
|
Dyspnea |
20 |
1.6 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue |
||
|
Arthralgia |
18 |
0 |
|
Myalgia |
16 |
0 |
|
Vascular |
||
|
Hypertension |
13 |
3.3 |
|
Metabolism and nutrition |
||
|
Weight increased |
12 |
1.6 |
Source: WELIREG Prescribing Information
*Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0
1 Includes fatigue and asthenia
2 Includes headache and migraine
3 Incudes dizziness and vertigo
4 Includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper and abdominal pain lower
5 Includes visual impairment, vision blurred, central retinal vein occlusion and retinal detachment includes bronchitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and viral upper respiratory infection
Abbreviations: NCI CTCAE, National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: The overall occurrence of side effects was similar in males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, racial differences in side effects cannot be determined.
- Age: The number of patients 65 years of age and older was small; therefore, differences in side effects among age groups cannot be determined.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 4. Side Effects by Demographic Subgroup
|
Subgroup |
WELIREG |
|
|---|---|---|
|
All Grades |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|
|
Age. years |
||
|
<65 |
59/59 (100) |
14/59 (23.7) |
|
≥65 |
2/2 (100) |
0 |
|
Sex |
||
|
Male |
29/29 (100) |
3/29 (10.3) |
|
Female |
32/32 (100) |
11/32 (34.3) |
|
Region |
||
|
United States |
48/48 (100) |
9/48 (18.7) |
|
Non-United States |
13/13 (100) |
5/13 (38.5) |
|
Race |
||
|
White |
55/55 (100) |
13/55 (23.6) |
|
Other |
6/6 (100) |
1/6 (16.7) |
|
Ethnicity |
||
|
Hispanic |
7/7 (100) |
2/7 (28.6) |
|
Not Hispanic or Unknown |
54/54 (100) |
12/54 (22.2) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
DEMOGRAPHICS SNAPSHOT
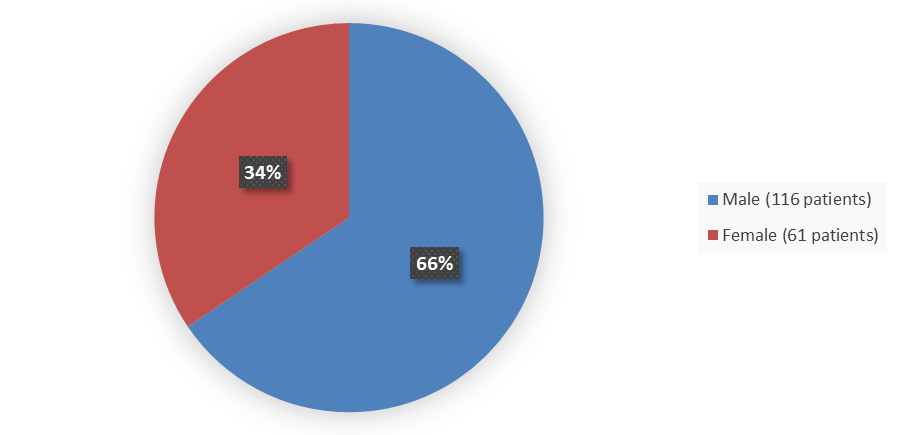
Figure 1 summarizes how many male and female patients were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the efficacy of WELIREG.
Figure 1 summarizes how many male and female patients were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the efficacy of WELIREG.
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Figure 2 summarizes how many patients by sex were in the combined trials used to evaluate the side effects of WELIREG.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Sex (Safety Population)
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the combined clinical trials used to evaluate the efficacy of WELIREG.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Race (Efficacy Population)
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
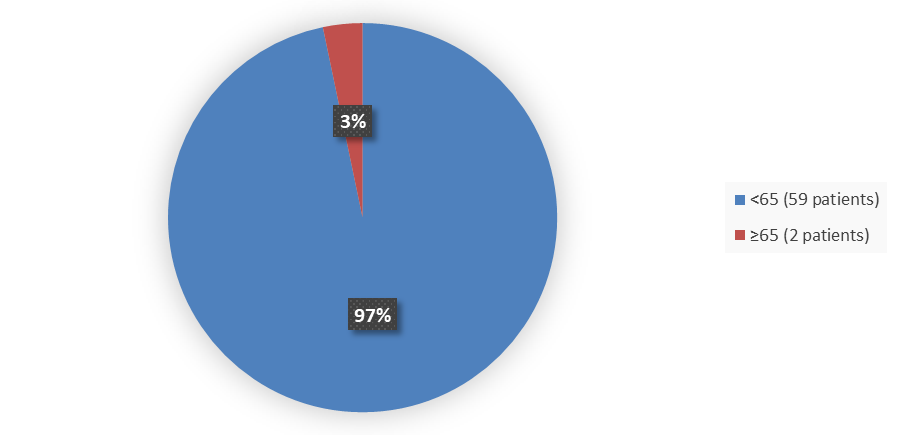
Figure 4 summarizes how many patients by age were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the efficacy of WELIREG.
Figure 4. Baseline Demographics by Age (Efficacy Population)
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Figure 5 summarizes how many patients by age were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the side effects of WELIREG.
Figure 5. Baseline Demographics by Age (Safety Population)
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
The benefit of WELIREG was evaluated in one single-arm clinical trial of 61 patients with VHL associated renal cell carcinoma that had not spread beyond the kidney. The benefit of WELIREG was evaluated by measuring if and how much the tumor size changed during treatment and how long that change lasted.
How were the trials designed?
The efficacy of WELIREG was evaluated in an open-label clinical trial in 61 patients with VHL-associated RCC diagnosed based on a VHL germline alteration and with at least one measurable solid tumor localized to the kidney as defined by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST) v1.1. Enrolled patients had other VHL-associated tumors including central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastomas and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (pNET). CNS hemangioblastomas and pNETs in these patients were diagnosed based on the presence of at least one measurable solid tumor in the brain/spine or pancreas, respectively. The study excluded patients with metastatic disease. Patients received WELIREG 120 mg once daily until their cancer worsened or they experienced unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome for the treatment of VHL-associated RCC was overall response rate (ORR), the percentage of people who had at least 30% shrinkage of total tumor size by radiology assessment per independent review committee (IRC). Additional efficacy outcomes included ORR in non-RCC tumors, and duration of response in RCC and non-RCC tumors.
The confirmed ORR in patients with VHL-associated RCC was 49% (30 out of 61 patients responded). The duration of response (DoR) was at least 12 months or longer in 17 (56%) of the 30 patients. In 24 patients with VHL-associated CNS hemangioblastomas who had at least one measurable solid lesion per IRC, the confirmed ORR was 63% and the DoR was at least 12 months or longer among 11 (73%) of 15 patients with response. Among 12 patients with VHL-associated pNET per IRC, 10 (83%) had ORR and DoR at 12 months was 50%.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
SAFETY: The types and severity of side effects that were reported during the clinical trials.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.