Drug Trials Snapshots: ALUNBRIG
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to ALUNBRIG Prescribing Information for complete information.
ALUNBRIG (brigatinib)
uh-lun-brig
Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Approval date: April 28, 2017
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
ALUNBRIG is a drug used to treat a type of lung cancer called non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that is advanced (metastatic). It is to be used in patients who have a specific gene mutation in the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene. It should be used in patients whose cancer has worsened after, or who could not tolerate treatment with, another drug called Xalkori (crizotinib).
ALUNBRIG was approved under FDA’s accelerated approval program, which provides earlier patient access to a promising new drug while the company continues to conduct clinical trials to confirm that the drug works well.
How is this drug used?
ALUNBRIG is a tablet that is taken once daily with or without food.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In the trial, approximately half of the 222 patients who received ALUNBRIG experienced cancer shrinkage of at least 30% which lasted about 14 months.
Approximately two-thirds of 18 patients who had measurable cancer lesions in the brain prior to taking ALUNBRIG experienced partial cancer shrinkage of the lesions in the brain.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Table below summarizes efficacy results for the clinical trial as evaluated by Independent Review Committee (IRC) and investigators.
Table 2. Efficacy Results in Trial 1
| Efficacy parameter | IRC Assessment | Investigator Assessment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 mg once daily arm (N=112) |
90→180 mg once daily arm (N=110) |
90 mg once daily arm (N=112) |
90→180 mg once daily arm (N=110) |
|
| Objective Response Rate (95% CI) | 48% (39-58) | 53% (43-62) | 45% (35-54) | 54% (44-63) |
| Complete Response, n (%) | 4 (3.6%) | 5 (4.5%) | 1 (0.9%) | 4 (3.6%) |
| Partial Response, n (%) | 50 (45%) | 53 (48%) | 49 (44%) | 55 (50%) |
| Duration of Response, median in months (95% CI) | 13.8 (7.4-NE) | 13.8 (9.3-NE) | 13.8 (5.6-13.8) | 11.1 (9.2-13.8) |
CI = Confidence Interval; NE = Not Estimable
ALUNBRIG Prescribing Information
Table below summarizes additional outcome measures (intracranial responses) as evaluated by the IRC.
Table 3. Intracranial Objective Response in Patients with Measurable Brain Metastases at Baseline in Trial 1
| Efficacy parameter | IRC Assessment | |
|---|---|---|
| 90 mg once daily arm (N=26) |
90→180 mg once daily arm (N=18) |
|
| Intracranial Objective Response Rate, (95% CI) | 42% (23-63) | 67% (41-87) |
| Complete Response, n (%) | 2 (7.7%) | 0 |
| Partial Response, n (%) | 9 (35%) | 12 (67%) |
| Duration of Intracranial Response, median (months) (range) | NE (1.9+ - 9.2+) | 5.6 (1.9+ - 9.2+) |
CI = Confidence Interval; NE = Not Estimable
ALUNBRIG Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: ALUNBRIG worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: The majority patients in the clinical trial were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in response among races could not be determined.
- Age: The majority of patients in the clinical trial were younger than 65 years of age. Differences in response to ALUNBRIG between patients below and above 65 years of age could not be determined.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Tables below summarize efficacy results by subgroup. These exploratory analyses should be interpreted with caution.
Table 4. Subgroup Analysis of Objective Response Rate by Sex
| Efficacy Parameter | Women | Men | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 mg N=62 |
90 →180 mg N=64 |
Total N=126 |
90 mg N=50 |
90 →180 mg N=46 |
Total N=96 |
||
| Confirmed Objective Response Ratea |
n (%) | 27 (43.5) | 37 (57.8) | 64 (50.8) | 23 (46.0) | 22 (47.8) | 45 (46.9) |
| 95% CIb | 31.0, 56.7 | 44.8, 70.1 | 41.7, 59.8 | 31.8, 60.7 | 32.9, 63.1 | 36.6, 57.3 | |
Table 5. Subgroup Analysis of Objective Response Rate by Race
| Efficacy Parameter | Asian | Non-Asian | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 mg N=39 |
90 →180 mg N=30 |
Total N=69 |
90 mg N=73 |
90 →180 mg N=80 |
Total N=153 |
||
| Confirmed Objective Response Ratea |
n (%) | 18 (46.2) | 18 (60.0) | 36 (52.2) | 32 (43.8) | 41 (51.3) | 73 (47.7) |
| 95% CIb | 30.1, 62.8 | 40.6, 77.3 | 39.8, 64.4 | 32.2, 55.9 | 39.8, 62.6 | 39.6, 55.9 | |
Table 6. Subgroup Analysis of Objective Response Rate by Age
| Efficacy Parameter | Age 18–64 Years | Age ≥65 Years | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 mg N=90 |
90 →180 mg N=80 |
Total N=170 |
90 mg N=22 |
90 →180 mg N=30 |
Total N=52 |
||
| Confirmed Objective Response Ratea |
n (%) | 37 (41.1) | 44 (55.0) | 81 (47.6) | 13 (59.1) | 15 (50.0) | 28 (53.8) |
| 95% CIb | 30.8, 52.0 | 43.5, 66.2 | 39.9, 55.4 | 36.4, 79.3 | 31.3, 68.7 | 39.5, 67.8 | |
CI = confidence interval;
aConfirmed objective response rate is defined as the proportion of the response evaluable patients who are confirmed to have achieved complete response or partial response per RECIST v1.1 after study drug initiation.
b The 95% CIs were calculated using the exact binomial method.
Adapted from FDA review
What are the possible side effects?
ALUNBRIG may cause serious side effects, including swelling (inflammation) of the lungs, high blood pressure, slow heartbeat, visual disturbance, high blood sugar and increase of pancreatic and muscle enzymes in the blood.
The most common side effects of ALUNBRIG are nausea, diarrhea, tiredness, cough and headache.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Tables below summarize adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, in the clinical trial.
Table 7. Adverse Reactions in ≥ 10% (All Grades) or ≥ 2% (Grade 3-4) of Patients by Dose Group in Trial 1
| Adverse Reactions | 90 mg once daily group N = 109 |
90→180 mg once daily group N = 110 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
| Eye Disorders | ||||
| Visual Disturbance† | 7 | 0 | 10 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 33 | 1 | 40 | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 19 | 0 | 38 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 24 | 2 | 23 | 0 |
| Constipation | 19 | 1 | 15 | 0 |
| Abdominal Pain‡ | 17 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| General Disorders And Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Fatigue§ | 29 | 2 | 36 | 0 |
| Pyrexia | 14 | 0 | 6 | 1 |
| Infections | ||||
| Pneumonia | 5 | 3‡‡ | 10 | 5‡‡ |
| Metabolism And Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Decreased Appetite | 22 | 1 | 15 | 1 |
| Musculoskeletal And Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Muscle Spasms | 12 | 0 | 17 | 0 |
| Back pain | 10 | 2 | 15 | 2 |
| Myalgia¶ | 9 | 0 | 15 | 1 |
| Arthralgia | 14 | 1 | 14 | 0 |
| Pain in extremity | 11 | 0 | 4 | 1 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Headache# | 28 | 0 | 27 | 1 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 11 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic And Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
| Cough | 18 | 0 | 34 | 0 |
| DyspneaÞ | 27 | 3 | 21 | 2‡‡ |
| ILD/Pneumonitis** | 4 | 2 | 9 | 3 |
| Hypoxia | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Skin And Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Rash†† | 15 | 2 | 24 | 4 |
| Vascular Disorders | ||||
| Hypertension | 11 | 6 | 21 | 6 |
*Per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.0
†Includes diplopia, photophobia, blurred vision, reduced visual acuity, visual impairment, vitreous floaters, visual field defect, macular edema, and vitreous detachment
‡Includes abdominal distension, abdominal pain, and epigastric discomfort
§Includes asthenia, fatigue
¶Includes musculoskeletal pain and myalgia
#Includes headache and sinus headache
ÞIncludes dyspnea and exertional dyspnea
**Includes interstitial lung disease and pneumonitis
††Includes acneiform dermatitis, exfoliative rash, rash, pruritic rash, and pustular rash
ALUNBRIG Prescribing Information
Table 8. Laboratory Abnormalities Occurring in >20% (All Grades) of Patients by Regimen in Trial 1
| Laboratory Abnormality | 90 mg once daily group N= 109 |
90→180 mg once daily group N=110 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) |
Grades 3-4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grades 3-4 (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||||
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 38 | 1 | 65 | 0 |
| Increased glucose† | 38 | 4 | 49 | 4 |
| Increased creatine phosphokinase | 27 | 3 | 48 | 12 |
| Increased lipase | 21 | 5 | 45 | 5 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 34 | 0 | 40 | 3 |
| Increased amylase | 27 | 4 | 39 | 3 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 15 | 1 | 29 | 1 |
| Decreased phosphorous | 15 | 2 | 23 | 4 |
| Prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time | 22 | 2 | 20 | 1 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Decreased hemoglobin | 23 | 1 | 40 | 1 |
| Decreased lymphocytes | 19 | 3 | 27 | 5 |
*Per CTCAE version 4.0
†Elevated blood insulin was also observed in both regimens
ALUNBRIG Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The risk of side effects was similar in men and women
- Race: The majority patients in the clinical trial were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The majority of patients in the clinical trial were younger than 65 years of age. Differences in side effects between patients below and above 65 years of age could not be determined.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize adverse events during the clinical trial by demographic subgroup. These exploratory analyses should be interpreted with caution.
Table 9. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events by Age
| 90 mg N=109 n (%) |
90→180 mg1 N=110 n (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65=""> N=842 n (%) |
≥ 65 N=22 n (%) |
65=""> N=80 n (%) |
≥ 65 N=30 n (%) |
|
| Any TEAE | 84 (97) | 22 (100) | 80 (100) | 30 (100) |
| Grade 3-4 TEAEs | 26 (31) | 12 (55) | 37 (46) | 15 (50) |
| Grade 5 TEAEs | 14 (17) | 4 (18) | 7 (9) | 2 (7) |
| Any SAE | 33 (39) | 8 (36) | 31 (39) | 13 (43) |
| TEAEs leading to discontinuation | 5 (6) | 2 | 7 (9) | 4 (13) |
1 The 180 mg regimen includes dosing at 90 mg daily for 7 days prior to escalation to 180 mg daily.
2 No AEs were reported in 3 patients 65="" years="" of="" age="" in="" arm="">
Table 10.Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events by Sex
| 90 mg N=109 n (%) |
90→180 mg1 N=110 n (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men N=472 |
Women N=59 |
Men N=46 |
Women N=64 |
|
| Any TEAE | 47 (94) | 59 (100) | (100) | (100) |
| Grade 3-4 TEAEs | 19 (40) | 19 (32) | 19 (41) | 33 (52) |
| Grade 5 TEAEs | 9 (19) | 9 (15) | 5 (11) | 4 (6) |
| Any SAE | 19 (40) | 22(37) | 21 (46) | 23 (36) |
| TEAEs leading to discontinuation | 4 (8.5) | 3 (5.1) | 7 (15) | 4 (6) |
1 The 180 mg regimen includes dosing at 90 mg daily for 7 days prior to escalation to 180 mg daily.
2 No TEAEs were reported in 3 male patients in Arm A.
Table 11.Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events by Race1
| 90 mg N=109 n (%) |
90→180 mg2 N=110 n (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White N=703 |
Asian N=393 |
White N=76 |
Asian N=30 |
|
| Any TEAE | 68 (97) | 38 (97) | 76 (100) | 30 (100) |
| Grade 3-4 TEAEs | 29 (41) | 9 (23) | 35 (46) | 14 (18) |
| Grade 5 TEAEs | 14 (20) | 4 (10) | 9 (12) | 0 |
| Any SAE | 28 (40) | 13 (33) | 32 (42) | 11 (14) |
| TEAEs leading to discontinuation | 4 (6) | 3 (8) | 9 (12) | 3 (3.9) |
1 There were 3 Black patients enrolled overall in Trial. Additionally, there were 2 patients of unknown race in Arm B. No meaningful analysis could be performed given the small number so these patients were excluded from the table.
2 The 180 mg regimen includes dosing at 90 mg daily for 7 days prior to escalation to 180 mg daily.
3 No TEAEs were reported in 2 White patients and one Asian patient.
FDA Review
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved ALUNBRIG based on evidence from one clinical trial of 222 patients with advanced, ALK positive NSCLC. The trial was conducted in the 94 trial centers in 18 countries in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
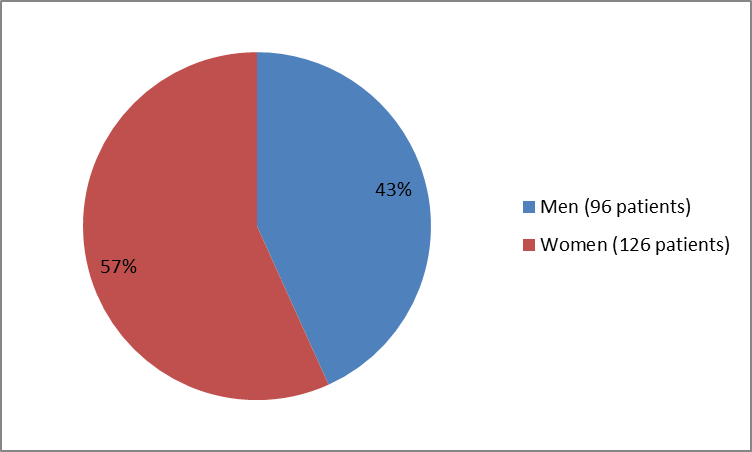
The figure below summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
FDA Review
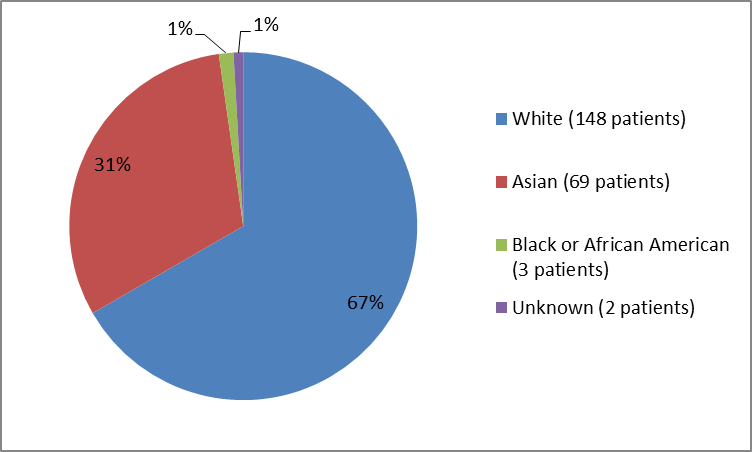
Figure 2 and Table 1 below summarize the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
FDA Review
Table 1. Demographics of Efficacy Trials by Race
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 148 | 67 |
| Asian | 69 | 31 |
| Black or African American | 3 | 1 |
| Unknown | 2 | 1 |
FDA Review
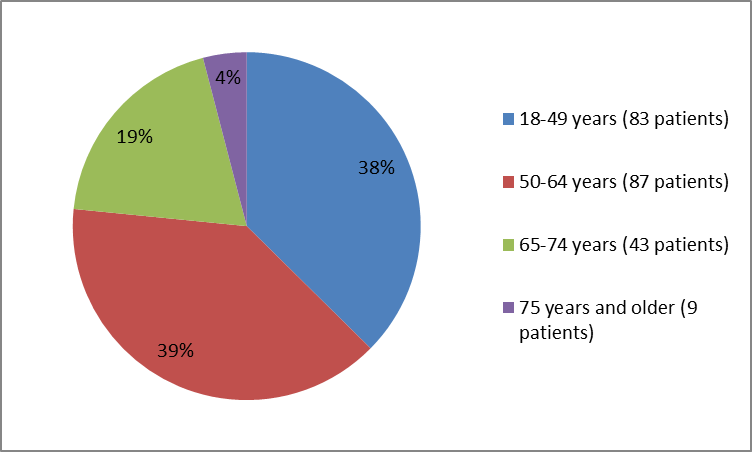
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics of patients in the clinical trials.
Table 12. Baseline Demographics of Patients in the Clinical Trial
| Demographic Parameters | ALUNBRIG N=222 |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Men | 96 (43.2) |
| Women | 126 (56.8) |
| Age (years) | |
| Mean (SD) | 53.4 (13.1) |
| Median (Range) | 54 (18,82) |
| Age Group (years) | |
| 18-49 | 83 (37.4) |
| 50-64 | 87 (39.2) |
| 65-74 | 43 (19.4) |
| ≥75 years | 9 (4.1) |
| Race | |
| White | 148 (66.7) |
| Asian | 69 (31.1) |
| Black or African American | 3 (1.4) |
| Unknown | 2 (0.9) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Hispanic or Latino | 13 (5.9) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 209 (94.1) |
FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of ALUNBRIG were evaluated in one clinical trial that enrolled patients with advanced NSCLC with the ALK mutation and who were previously treated with another drug called Xalkori (crizotinib). All patients received ALUNBRIG using one of two different dosing schedules: approximately half of the patients received 90 mg of ALUNBRIG every day and half received 90 mg daily for 7 days and then continued 180 mg daily. Treatment continued until disease progression or patients experienced unacceptable toxicity.
The benefit of ALUNBRIG was evaluated by measuring if and how much the tumor size changed during treatment and how long that response lasted.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of ALUNBRIG were established in one, two-arm, open label multicenter clinical trial. The trial enrolled adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC, who have progressed on crizotinib. Patients received ALUNBRIG either 90 mg once daily or 180 mg once daily following a 7-day lead-in at 90 mg once daily.
The efficacy outcome measure was objective response rate (ORR) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST v1.1) as evaluated per Independent Review Committee (IRC) and investigators.
Additional outcome measures as evaluated by the IRC included duration of response (DOR), intracranial objective response rate, and intracranial duration of response.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION