Rapid Response Teams (RRTs)
On this page:
- FDA Rapid Response Teams YouTube Video (Recommended Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge)
- What are the Rapid Response Teams (RRTs)?
- Why establish RRTs?
- Which states currently have RRTs?
- How can I obtain a copy of the RRT Best Practices Manual?
- What funding is in place to support RRTs?
- What animal and human food emergencies have RRTs assisted with?
- What is Domestic Mutual Reliance
- Who do I contact for more information?
- RRT CAP Fact Sheet (Version November 2023) (PDF - 121KB)
FDA Rapid Response Teams YouTube Video
What are the Rapid Response Teams (RRTs)?
RRTs are multi-agency, multi-disciplinary teams that operate using Incident Command System (ICS)/National Incident Management System (NIMS) principles and a Unified Command structure to respond to human and animal food emergencies.
Why establish RRTs?
The desired outcome of RRT development is to minimize the time between agency notification of a human or animal food contamination event and implementation of effective control measures. To accomplish this, RRTs develop and maintain processes to:
- Prepare for and effectively respond to foodborne illness outbreaks and other food emergencies.
- Enhance intra-agency and interagency collaboration and communication.
- Jointly train and exercise staff to be ready to respond to events when they occur.
- Identify potential preventive practices to reduce foodborne illness and injury.
- Establish national best practices and tools that can be shared with other states to improve their response to food emergencies.
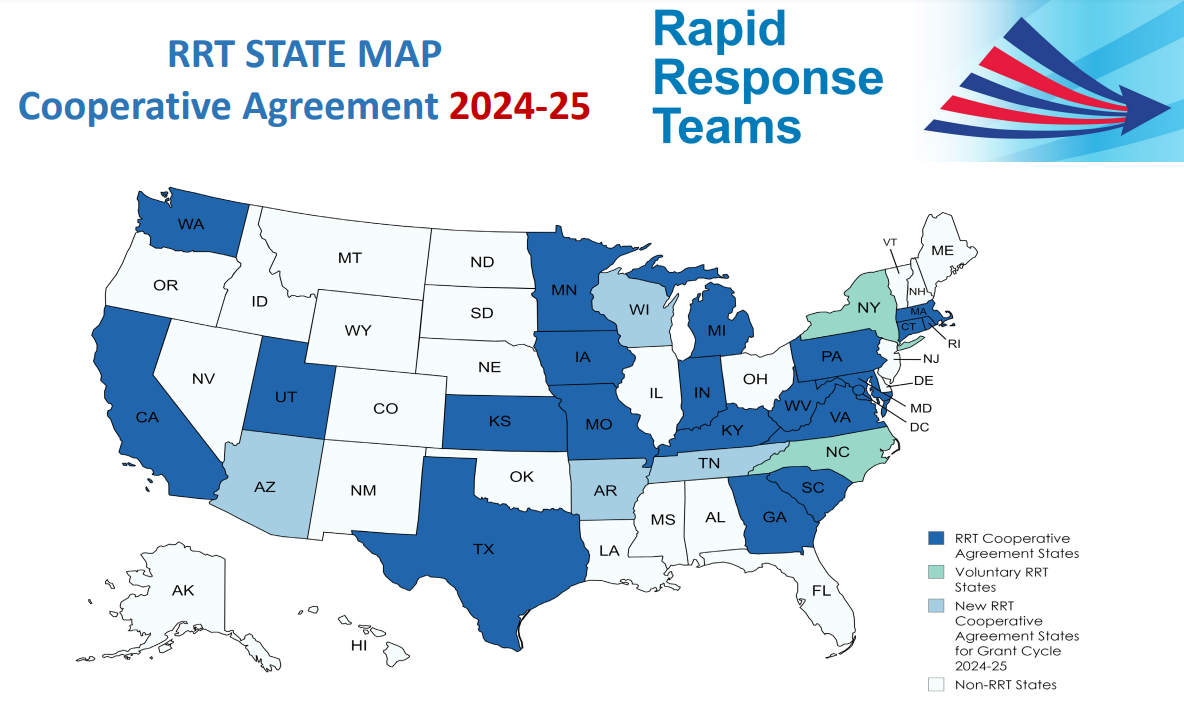
Which states currently have RRTs?
- United States Map displaying 24 FDA funded Rapid Response Team cooperative agreement states: AR, AZ, CA, CT, GA, IA, IN, KS, KY, MA, MD, MI, MN, MO, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VA, WA, WI, WV.
- NC and NY participate in a voluntary, non-funded capacity.
- Over $5.6M in funding under this cooperative agreement program
How can I obtain a copy of the RRT Best Practices Manual?
The RRT Best Practices Manual features tools that can be used by programs to improve key areas of response such as communication, traceback and traceforward, laboratory analysis, and joint investigations and inspections. It also establishes metrics for rapid response capabilities that allow RRTs to assess their status, identify improvement plans, and quantify accomplishments and impact.
The full version of the RRT Best Practices Manual (2017 Edition) can be obtained by clicking here.
A companion document to the RRT Best Practices Manual is the RRT Capacity Building and Mentorship Framework. This document provides a three-phase framework for incremental RRT capacity building and can be applied by any State/Division-District wishing to establish a RRT with functional rapid response capabilities aligned with the RRT Best Practices Manual and the NIMS preparedness cycle.
The full version of the RRT Capacity Building and Mentorship Framework can be obtained by clicking here.
What funding is in place to support RRTs?
FDA provides multi-year cooperative agreements to states to form and maintain RRTs. These cooperative agreements require RRTs to engage partners across disciplines and jurisdictions to build core capabilities and explore innovative approaches to response.
What animal and human food emergencies have RRTs assisted with?
- FDA and States use Rapid Response Teams Approach to Combat Foodborne Illness through Domestic Mutual Reliance (Food Safety Magazine, April 2021)
- Meeting summary and posters from the 2020 RRT Computer-to-Computer (C2C) and 2019 RRT Face-to-Face (F2F) meeting (Association of Food and Drug Officials)
- All hands on deck: Changing roles around COVID Response (Washington State Department of Agriculture Blog, March 2021)
- Virginia’s Collaborative Investigation Cracks the Case (CDC OutbreakNet Enhanced Success Story, January 2021)
- Outbreak Investigation of Scombrotoxin Fish Poisoning Illnesses in the United States Linked to Yellowfin Tuna Imported from Vietnam – 2019 (Journal of Food Protection, January 2021)
- Lessons Learned from a Decade of Investigations of Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli Outbreaks Linked to Leafy Greens, United States and Canada (Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 2020).
- Outbreak of Norovirus Gastroenteritis Associated With Ice Cream Contaminated by Frozen Raspberries From China—Minnesota, United States, 2016 (Clinical Infectious Diseases, June 2020)
- Successful Collaboration Protects Rhode Island Residents from Foodborne Illness (APHL Success Story, May 2020)
- Listeria monocytogenes Occurrence and Adherence to Recommendations: Small and Large Retail Delicatessens in Iowa (Food Protection Trends, September 2020)
- Virginia Hepatitis A Pandora Radio Campaign A Success Story of Interagency Collaboration (AFDO Blog Post, September 2019)
- Overview of Leafy Greens - Related Food Safety Incidents with a California Link (Journal of Food Protection, March 2019)
- RRT Testimonials - Reflections on 10 Years of RRTs (2008 - 2018) (March 2019)
- Responding to Harvey and Irma: Rapid Response Teams Take Action (Food Safety Magazine April/May 2018 Issue)
- Local Rapid Response Team Deters Deliberate Food Poisoning (NACCHO Blog Post September 2017)
- Response to animal feed contamination quick, coordinated (WSDA Blog Post September 2017)
- Multistate outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infections linked to whole apples used in commercially produced, prepackaged caramel apples: United States, 2014-2015. (Epidemiology and Infection Journal, January 2017)
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Detection of Ongoing Listeria Contamination at a Restaurant, Rhode Island, USA, 2014 (Emerging Infectious Diseases Journal, August 2016)
- Stopping Listeria required an arsenal of tools and an army of experts (APHL Blog post June 2016)
- Regional investigation of a cyclosporiasis outbreak linked to imported romaine lettuce – Nebraska and Iowa, June–August 2013 (Journal of Epidemiology and Infection, July 2016)
- Outbreak of Foodborne Botulism Associated with Improperly Jarred Pesto — Ohio and California, 2014 (MMWR Article, February 2016)
- Outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infections linked to a pasteurized ice cream product served to hospitalized patients (Journal of Epidemiology and Infection, December 2015)
- Where the Rubber Meets the Road: RRTs in Action (Food Safety Magazine Aug/Sep 2015 issue)
- Creating the Rapid Response Road Map: Collaboration Points the Way Forward (Food Safety Magazine Oct/Nov 2015 issue)
- Outbreak of Salmonella enterica serotype Infantis infection in humans linked to dry dog food in the United States and Canada, 2012 (March 2014, Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association)
- Use of Global Trade Item Numbers in the Investigation of a Salmonella Newport Outbreak Associated with Blueberries in Minnesota, 2010 (May 2013 Journal of Food Protection)
- Use of traceback methods to confirm the source of a multistate Escherichia coli 0157:H7 outbreak due to in-shell hazelnuts (February 2012, Journal of Food Protection)
- CalFERT Environmental Investigation Reports (2012-present)
What is Domestic Mutual Reliance
Domestic mutual reliance is a seamless partnership that enables the FDA and states with comparable regulatory public health systems, as trusted partners, to rely on, coordinate with, and leverage one another's work, data, and actions to meet the public health goal of a safe national food supply.
Who do I contact for more information?
More information can be found in the Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA).
Specific questions on this program can be directed to the appropriate Office of Partnerships' contact within the Division of Partnership Investments and Agreements. Please visit the Office of Partnerships Contacts webpage to obtain a downloaded version of the staffing roster.