Drug Trial Snapshot: XOFLUZA
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the XOFLUZA Package Insert for complete information.
XOFLUZA (baloxavir marboxil)
zo-FLEW-zuh
Genentech USA, Inc.
Approval date: October 24, 2018
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
XOFLUZA is a drug to treat the flu (influenza) in people 12 years of age and older who have had flu symptoms for no more than 48 hours.
How is this drug used?
XOFLUZA is a tablet taken as a single dose by mouth within 48 hours of flu symptoms.
The dose depends on the patient’s weight.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Patients treated with XOFLUZA had a shorter time to relieve symptoms compared with patients treated with placebo.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The figures below summarize efficacy results for the evaluated patients in Trials 1 and 2. The primary outcome was time to alleviation of symptoms.
Table 2. Time to Alleviation of Symptoms after Single Dose in Adult Subjects with Acute Uncomplicated Influenza in Trial 1 (Median Hours)
|
|
XOFLUZA 40 mg |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Adults (20 to 64 Years of Age) |
50 hours2 |
78 hours |
1CI: Confidence interval
2XOFLUZA treatment resulted in a statistically significant shorter time to alleviation of symptoms compared to placebo using the Gehan-Breslow’s generalized Wilcoxon test (p-value: 0.014, adjusted for multiplicity). The primary analysis using the Cox Proportional Hazards Model did not reach statistical significance (p-value: 0.165).
Table 3. Time to Alleviation of Symptoms after Single Dose in Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Acute Uncomplicated Influenza in Trial 2 (Median Hours)
|
|
XOFLUZA 40 mg or 80 mg1 |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Subjects (≥ 12 Years of Age) |
54 hours3 |
80 hours |
1Dosing was based on weight. Subjects weighing < 80 kg received a single 40 mg dose and subjects ≥ 80 kg received a single 80 mg dose.
2CI: Confidence interval
3XOFLUZA treatment resulted in a statistically significant shorter time to alleviation of symptoms compared to placebo using the Peto-Prentice’s generalized Wilcoxon test (p-value: <0.001).
XOFLUZA Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: XOFLUZA worked similarly in males and females.
- Race: XOFLUZA worked similarly among Whites and Asians. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in how XOFLUZA worked among other races could not be determined.
- Age: XOFLUZA worked similarly among patients 12 to 17 years of age and those 18 years of age and older.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes efficacy results by sex, race and age. The majority of patients were White and Asian, and the number of patients in all other races was limited. Therefore, racial subgroup differences were investigated between Whites and Asians.
Table 4. Median Time to Alleviation of Symptoms after Single Dose in Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Acute Uncomplicated Influenza in Trials 1 and 2
|
Time to Alleviation of Symptoms |
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
|
Sex |
||||
|
Female |
N=40 |
N=39 |
N=224 |
N=110 |
|
Median time in hours |
54 |
93 |
63 |
87 |
|
Male |
N=60 |
N=61 |
N=231 |
N=120 |
|
Median time in hours |
48 |
69 |
48 |
74 |
|
Race |
||||
|
White |
N=0 |
N=0 |
N=85 |
N=40 |
|
Median time in hours |
-- |
-- |
93 |
126 |
|
Asian |
N=100 |
N=100 |
N=348 |
N=177 |
|
Median time in hours |
50 |
78 |
46 |
78 |
|
Age |
||||
|
Adolescents (age 12 to 17) |
N=0 |
N=0 |
N=63 |
N=27 |
|
Median time in hours |
-- |
-- |
54 |
93 |
|
Adults (≥18 years of age) |
N=100 |
N=100 |
N=392 |
N=203 |
|
Median time in hours |
50 |
78 |
54 |
79 |
FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effects are diarrhea, bronchitis, common cold (nasopharyngitis), headache, and nausea
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in patients with uncomplicated influenza in combined trials (safety population).
Table 5. Incidence of Adverse Events Occurring in Greater Than or Equal to 1% of Subjects Receiving XOFLUZA in the Acute Uncomplicated Influenza Trials
|
Adverse Event |
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Diarrhea |
3% |
5% |
|
Bronchitis |
2% |
4% |
|
Nausea |
1% |
1% |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
1% |
1% |
|
Headache |
1% |
2% |
XOFLUZA Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in males and females.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar in Whites and Asians. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in the occurrence of side effects among other races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects among patients 12 to 17 years of age and those older than 18 years of age was similar.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes the occurrence of the most common adverse reaction, diarrhea, by subgroup.
Table 6. Subgroup Analysis of Diarrhea (safety population)
|
Demographic Characteristic |
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Sex |
||
|
Men |
9/355 (3) |
7/207 (3) |
|
Women |
11/355 (3) |
12/202 (6) |
|
Race |
||
|
White |
8/198 (4) |
2/98 (2) |
|
Black or African American |
0/40 (0) |
1/24 (4) |
|
Asian |
12/464 (3) |
16/284 (6) |
|
Other |
0/8 (0) |
0/3 (0) |
|
Age Group |
||
|
< 18 years |
3/76 (4) |
2/41 (5) |
|
> 18 years |
17/634 (3) |
17/368 (5) |
Clinical Trial Data
WHO WAS IN THE STUDIES?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved XOFLUZA based on evidence from two clinical trials (Trial 1/1518T0821 and Trial 2/NCT02954354) of 1119 patients with influenza-like illness. Trial 1 was conducted in Japan. Trial 2 was conducted in Japan and the United States.
Demographics of the patients who provided data for evaluation of benefits (efficacy population) are presented in Table 8, under the MORE INFO section.
The population that provided data for side effects of XOFLUZA (safety population) is presented below.
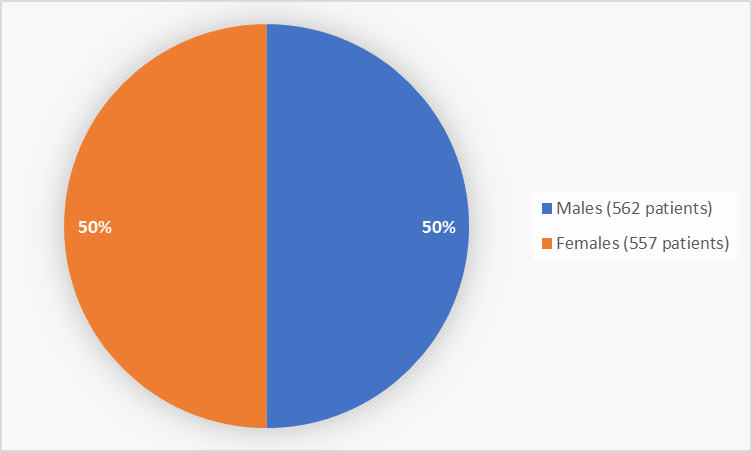
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trials used to evaluate safety.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (safety population)
FDA Review
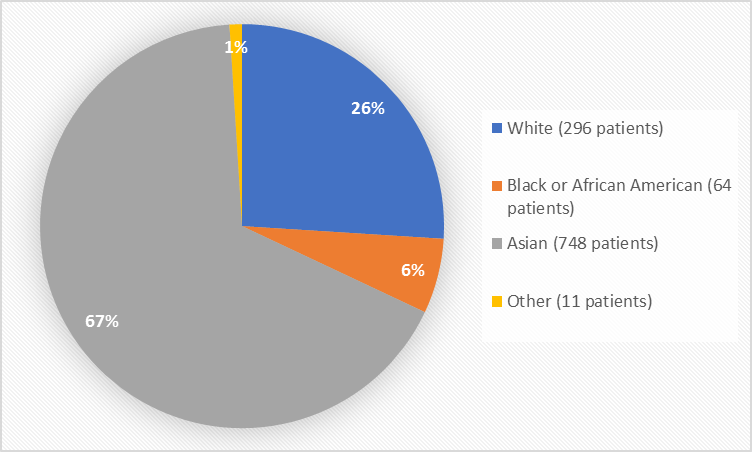
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials used to evaluate safety.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
FDA Review
Table 1. Demographics of Efficacy Trials by Race
|
Race |
Number of Patients |
Percentage of Patients |
|---|---|---|
|
White |
296 |
26% |
|
Black or African American |
64 |
6% |
|
Asian |
748 |
67% |
|
Other |
11 |
6% |
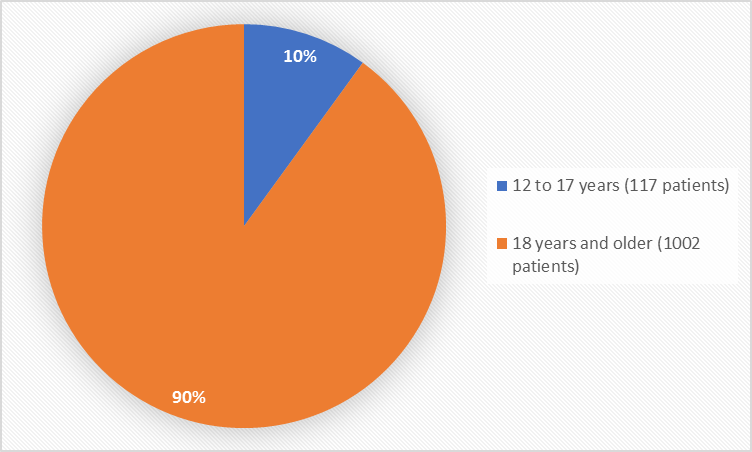
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age in the clinical trials used to evaluate safety.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Clinical Trial Data
Who participated in the trials
The table below summarizes the demographics of the safety population.
Table 7. Baseline Demographics of the Safety Population
|
Demographic Characteristic |
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 |
TOTAL |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
(N = 1119) |
|
|
Sex |
|||||
|
Men |
60 (60) |
61 (61) |
295(48) |
146 (47) |
562 (50) |
|
Women |
40 (40) |
39 (39) |
315 (52) |
163 (53) |
557 (50) |
|
Race |
|||||
|
White |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
198 (33) |
98 (32) |
296 (26) |
|
Black or African American |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
40 (7) |
24 (8) |
64 (6) |
|
Asian |
100 (100) |
100 (100) |
364 (60) |
184 (60) |
748 (67) |
|
Other |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
8 (1) |
3 (1) |
11 (1) |
|
Age |
|||||
|
>12 to < 17 years |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
76 (12) |
41 (13) |
117 (10) |
|
> 18 to < 29 years |
27 (27) |
28 (28) |
184 (30) |
88 (28) |
327 (29) |
|
> 30 to < 39 years |
30 (30) |
28 (28) |
138 (23) |
68 (22) |
264 (24) |
|
> 40 to < 49 years |
28 (28) |
32 (32) |
123 (20) |
58 (19) |
241 (22) |
|
> 50 to < 59 years |
11 (11) |
9 (9) |
74 (12) |
43 (14) |
137 (12) |
|
> 60 to < 64 years |
4 (4) |
3 (3) |
15 (2) |
11 (4) |
33 (3) |
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
Mean (SD) |
37.3 (10.6) |
37.4 (10.6) |
33.6 (13.1) |
34.2 (13.9) |
35.6 (12.1) |
|
Median |
38 |
37 |
33 |
33 |
35 |
|
Min, Max |
20, 63 |
20, 64 |
12, 64 |
12, 64 |
12, 64 |
|
Ethnicity |
|||||
|
Hispanic |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
116 (19) |
47 (15) |
163 (15) |
|
Not Hispanic |
100 (100) |
100 (100) |
494 (81) |
262 (85) |
956 (85) |
|
Region |
|||||
|
Asia |
100 (100) |
100 (100) |
355 (58%) |
180 (58%) |
735 (66) |
|
United States |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
255 (42%) |
129 (42%) |
384 (34) |
Clinical Trial Data
The table below summarizes the demographics of the efficacy population.
Table 8. Baseline Demographics of the Efficacy Population
|
Demographic Characteristic |
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
XOFLUZA |
Placebo |
|
|
Sex |
||||
|
Men |
60 (60) |
61 (61) |
232(51) |
120 (52) |
|
Women |
40 (40) |
39 (39) |
224 (49) |
111 (48) |
|
Race |
||||
|
White |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
85 (19) |
40 (17) |
|
Black or African American |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
18 (4) |
11 (5) |
|
Asian |
100 (100) |
100 (100) |
349 (77) |
178 (77) |
|
Other |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
4 (1) |
2 (1) |
|
Age |
||||
|
>12 to < 19 years |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
80 (18) |
38 (17) |
|
> 20 to < 29 years |
27 (27) |
28 (28) |
121 (27) |
61 (26) |
|
> 30 to < 39 years |
30 (30) |
28 (28) |
92 (20) |
47 (20) |
|
> 40 to < 49 years |
28 (28) |
32 (32) |
97 (21) |
48 (21) |
|
> 50 to < 59 years |
11 (11) |
9 (9) |
52 (11) |
30 (13) |
|
> 60 to < 64 years |
4 (4) |
3 (3) |
14 (3) |
7 (3) |
|
Age (years) |
||||
|
Mean (SD) |
37.3 (10.6) |
37.4 (10.6) |
33.5 (13.5) |
33.9 (13.7) |
|
Median |
38 |
37 |
32 |
33 |
|
Min, Max |
20, 63 |
20, 64 |
12, 64 |
12, 64 |
|
Ethnicity |
||||
|
Hispanic |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
32 (7) |
11 (5) |
|
Not Hispanic |
100 (100) |
100 (100) |
424 (93) |
220 (95) |
|
Region |
||||
|
Asia |
100 (100) |
100 (100) |
343 (75) |
175 (76) |
|
United States |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
113 (25) |
56 (24) |
Clinical Trial Data
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of XOFLUZA were evaluated in two clinical trials in adult and pediatric patients with uncomplicated influenza.
Trial 1 enrolled adult patients 20 to 64 years old who had symptoms of flu for no more than 48 hours. Patients were assigned to receive either a single dose of XOFLUZA or placebo by mouth. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed. The benefit of XOFLUZA was assessed based on the time patients reported all seven symptoms (cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, headache, fever, muscle pain, and tiredness) gone or mild for at least 21.5 hours, comparing the XOFLUZA and placebo groups.
Trial 2 enrolled adult and adolescent patients 12 to 64 years old who had symptoms of flu for not more than 48 hours. Adult patients were assigned to receive either XOFLUZA on Day 1 followed by placebo on Days 2 – 5, placebo as a twice daily dose by mouth for 5 days, or oseltamivir (a medication used to treat and prevent influenza) by mouth twice a day for 5 days. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed. The benefit of XOFLUZA was assessed based on the time patients reported all seven symptoms (cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, headache, fever, muscle pain, and tiredness) gone or mild for at least 21.5 hours, comparing the XOFLUZA and placebo groups.
How were the trials designed?
The efficacy and safety of XOFLUZA were evaluated in two randomized, double-blind clinical trials.
Trial 1 was a dose-finding trial in adult patients aged 20 to 64 years with uncomplicated influenza. Patients were randomized to receive a single oral dose of XOFLUZA or placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint was time to alleviation of symptoms defined as the time when all seven symptoms (cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, headache, fever, myalgia, and fatigue) had been assessed by patients as none or mild for a duration of at least 21.5 hours.
Trial 2 enrolled adult and adolescent patients 12 to 64 years of age weighing at least 40 kg. Adults were randomized to receive XOFLUZA or placebo as a single oral dose, or oseltamivir twice a day for 5 days. Patients in the XOFLUZA and placebo arms received a placebo for the duration of oseltamivir treatment. Adolescent patients (12 to less than 20 years of age) were randomized to receive XOFLUZA or placebo as a single oral dose. The primary efficacy endpoint was time to alleviation of symptoms defined as the time when all seven symptoms (cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, headache, fever, myalgia, and fatigue) had been assessed by patients as none or mild for a duration of at least 21.5 hours.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.