2023 FDA Science Forum
Examination of the Effect of Black Cohosh on the Efficacy of Risedronate on Bone Mineral Density in an Ovariectomized Rat Model
- Authors:
- Center:
-
Contributing OfficeNational Center for Toxicological Research
Abstract
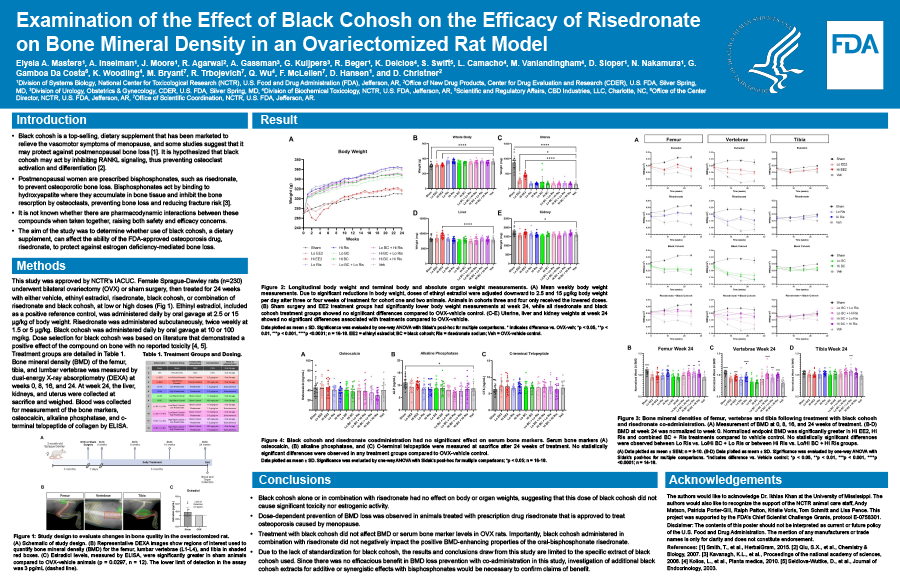
Black cohosh is a top-selling, dietary supplement that has been marketed to relieve the vasomotor symptoms of menopause, and some studies have shown that it may protect against postmenopausal bone loss. Postmenopausal women are also frequently prescribed bisphosphonates, such as risedronate, to prevent osteoporotic bone loss. For those women using both compounds, potential pharmacodynamic interactions are unknown. The aim of the study was to determine whether use of black cohosh can affect the ability of risedronate to protect against estrogen deficiency-mediated bone loss using an established model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Female Sprague-Dawley rats (n=230) at six months of age underwent bilateral ovariectomy or sham surgery, followed by 24 weeks of treatment with either vehicle or test article. Test articles include, ethinyl estradiol as a positive control at 2.5 and 15.0 ug/kg·bw, risedronate at 1.5 and 5.0 ug/kg·bw, black cohosh at 10 and 100 ug/kg·bw, or a combination of risedronate and black cohosh, at low or high doses. Bone mineral density (BMD) of the femur, tibia, and lumbar vertebrae was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). Body weight was measured weekly and endpoint organ weight was recorded at week 24. Body weights in the vehicle control and treatment groups were increased vs. estradiol and sham surgery groups from week 0 through week 24. At week 24, BMD in the high estradiol, high risedronate and combined black cohosh and risedronate treatment groups were significantly increased compared to vehicle control. However, no statistically significant differences were observed with black cohosh treatment alone, nor did the combination of black cohosh and risedronate treatment significantly increase BMD compared to risedronate treatment alone. Ultimately, the combination with black cohosh with risedronate did not negatively impact the positive BMD-enhancing properties of the bisphosphonate under our experimental conditions. Continued work should investigate bone histomorphometry and biomechanical testing to explore additive or synergistic effects of combined black cohosh and risedronate in the prevention of post-menopausal bone loss.